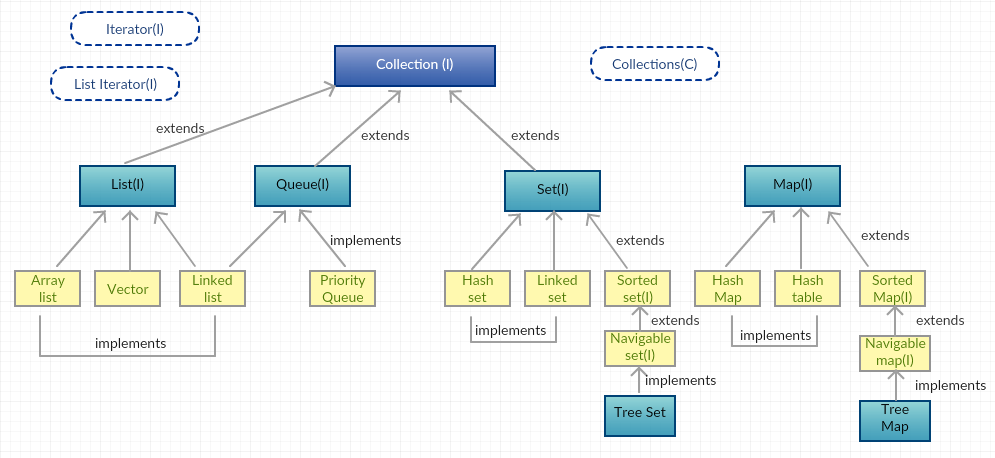
Description
Description
In Java Collections, all the elements are stored as object type. Whenever an element is retrieved from the collection the element will be in an object type and down casting has to be done. The collection doesn’t have any limit of size. It can grow dynamically. The Java Collections API provides several behaviors through which elements of collection can be accessed.
Collection framework classes either use array underneath or use more complex data structure. When an array is simply an array. Array does not have methods such as the ones provided by Collection classes.
For more detailed overview on array click here click here .
- Array is Fixed in Size. Where , Collection is Grow able in nature
- Array stores homogeneous data . Where, Collection store both homogeneous as well as Heterogeneous data.
- In Array , there are no underlined Data Structures, whereas ,Collection has Underlined DS.
- Array is recommended in performance , whereas Collection is not.
- Array use more memory space compare to Collection.
 Description
Description
List is a type of Java Collections.
For more detailed overview on interface click here.
- List interface defines standards for storing elements in the list format.
- It stores elements sequentially. Elements are auto indexed.
- Gets the elements based on index.
- Stores null object.
- Stores duplicate element.
- ArrayList ,vector and linked list implements List interface.
- LinkedList is both List and Queue.
- Vector is thread safe.
 Example
Example
The following is an example for the list.
[java]
package com.spl.collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
public class List {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Program starts");
ArrayList list=new ArrayList();
list.add("Sample");
list.add(12);
list.add(true);
list.add(null);
list.add(12);
list.add(new A());
System.out.println("ArrayList size="+list.size());
System.out.println("ArrayList elements-using for each loop");
for(Object obj:list)
{
System.out.println("Element="+obj);
}
System.out.println("ArrayList elements-using for loop");
for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++)
{
System.out.println(i+"th element="+list.get(i));
}
list.add(4,"24");
System.out.println("After inserting"+list);
list.set(4, "test");
System.out.println("After updating"+list);
ArrayList list1=new ArrayList();
list1.add(78);
list1.add(90);
list1.add(12);
list.addAll(list1);
System.out.println("After adding list1 to list="+list);
Collections.sort(list1);
System.out.println("Sorted List="+list1);
System.out.println("Program ends");
}
}
class A
{
}
[/java]
Output:
When compile the code following is the result will be displayed.
[c]
Program starts
ArrayList size=6
ArrayList elements-using for each loop
Element=Sample
Element=12
Element=true
Element=null
Element=12
Element=com.spl.collection.A@c21495
ArrayList elements-using for loop
0th element=Sample
1th element=12
2th element=true
3th element=null
4th element=12
5th element=com.spl.collection.A@c21495
After inserting[Sample, 12, true, null, 24, 12 com.spl.collection.A@c21495]
After updating[Sample, 12, true, null, test, 12 com.spl.collection.A@c21495]
After adding list1 to list=[Sample, 12, true, null, test, 12 com.spl.collection.A@c21495]
Program ends
[/c]
- ArrayList uses internally dynamic array to store the elements where as LinkedList uses doubly linked list
- ArrayList internally uses array that's why manipulation is slow where as LinkedList manipulation is fast why because it uses doubly linked list
 Description
Description
Set is a type of collection.
- Elements are stored randomly.
- No index for elements.
- Null is allowed.
- Duplicate elements are not allowed.
- Set is a unique collection of elements.
- Hashset,LinkedSet and Tree set implements set interface.
- Set defines standards to store elements uniquely.
- Set elements are referred using iterator.
- Java Collection provides an iterator object, to iterate the elements of the collection.
- Iterator can be used on list type,queue type and set type.
- Iterator provides a method by name "next" to get next element from collection.
- The hasNext() method returns true if the collection contains next element otherwise false.
- The remove() method removes the element from collection.
 Example
Example
The following is an example for the set.
[java]
package com.spl.collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class Set {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Program starts");
HashSet set=new HashSet();
set.add("Sample");
set.add(12);
set.add(true);
set.add(null);
set.add(12);
set.add(new A1());
System.out.println("ArrayList size="+set.size());
set.add("24");
System.out.println("After inserting"+set);
ArrayList set1=new ArrayList();
set1.add("SPLessons");
set1.add(90);
set.addAll(set1);
System.out.println("After adding list1 to list="+set);
Iterator itr=set.iterator();
while (itr.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(itr.next());
}
System.out.println("Program ends");
}
}
class A1
{
}
[/java]
The main difference between the list and set is that Listcan contain duplicate elements whereas Set contains unique elements only.
Output:
When compile the code following is the result.
[c]
Program starts
ArrayList size=5
After inserting[null, com.spl.collection.A1@ififba0, Sample, 24, true, 12]
After adding list1 to list=[SPLessons, null, com.spl.collection.A1@ififba0, Sample, 24, true, 12, 90]
SPLessons
null
com.spl.collection.A1@ififba0
Sample
24
true
12
90
Program ends
[/c]
 Description
Description
Queue defines standard to store elements in FIFO. Queue is a type of Java Collections.
- Elements are stored randomly.
- No index for elements.
- Duplicate elements are allowed.
- All elements are added at rear.
- Priority Queue, LinkedList implements Queue.
- Elements are referred in FIFO.
- Null value is not allowed.
- The priority queue class stores an element in a random order.
- Before storing element Priority Queue compares and stores it in natural sorting order.
- Whenever user print Priority Queue reference variable it prints the element of the queue randomly.
- Head element of the queue can be obtained by using a method poll().
- The poll() method removes head element from the queue.
- For each poll() method execution queue size will be reduced.
- To retrieve or see the current head element user can use peek() method.
 Note
Note
Note
- Whenever user add an element to Priority Queue element should be of type Comparable.
- Its an interface available in java.lang package which defines a standard to compare any 2 same type object.?
 Example
Example
The following is an example for the queue.
[java]
package com.spl.collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class Queue {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Program starts");
PriorityQueue queue=new PriorityQueue();
queue.add(12);
queue.add(23);
queue.add(45);
queue.add(67);
queue.add(23);
System.out.println("queue size="+queue.size());
System.out.println("queue elements="+queue);
System.out.println("Head element="+queue.poll());
System.out.println("queue size="+queue.size());
System.out.println("Current head element="+queue.peek());
System.out.println("queue size="+queue.size());
System.out.println("Program ends");
}
}
[/java]
Output:
When compile the code following is the result.
[c]Program starts
queue size=5
queue elements=[12, 23, 45, 67, 23]
Head elements=12
queue size=4
Current head element=23
queue size=4
Program ends[/c]
 Description
Description
A map is a collection of “key -value” pairs where a key is mapped to the value whenever an element is added.
- Key is an index for the value key is a unique type of collection which doesn’t allow duplicate elements.
- Values can have duplicates element.
- Both key and value can be null.
 Example
Example
The following is an example for the map.
[java]
package com.spl.collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class HashMapEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Program starts");
HashMap map1=new HashMap();
map1.put(12,true);
map1.put("demo", 23);
map1.put(false, 4.5);
map1.put(new A2(), new B2());
System.out.println(map1);
System.out.println("Map size="+map1.size());
map1.put(12, false);
System.out.println("After updating="+map1);
System.out.println("demo value="+map1.get("demo"));
System.out.println("Program ends");
}
}
class A2
{
}
class B2
{
}
[/java]
Output:
When compile the code following is the result.
[c]
Program starts
{demo=23, false=4.5, com.spl.collecion.A2@ififba0=com.spl.collection.B2@15f5897, 12=true}
Map size=4
After updating={demo=23, false=4.5, com.spl.collecion.A2@ififba0=com.spl.collection.B2@15f5897, 12=true}
demo value=23
Program ends
[/c]
The Hashtable and HashMap are utilized to store information in key and value form. Both will use hashing technique to store unique keys. The following are the some main difference.
- HashMap is non synchronized where as Hashtable is synchronized.
- Hahtable is a legacy class where as hashmap is new.
- HashMap uses iterator where as HashTable uses enumerator and iterator.
 Description
Description
Collection API provides a class by name collections which contains sort method used to sort any type of collection.
- The sort() method sorts the element only, if its comparable Type.The sort method calls compareTo() method of comparable type object and sorts element of collection.
- String class and wrapper classes are comparable type hence we can sort any collection which contains string or wrapper type object.
 Example
Example
The following is an example for the sorting.
[java]
package com.spl.collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
public class AdCollection {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Program starts");
ArrayList list=new ArrayList();
list.add(new Student(1234, 23.45));
list.add(new Student(2345, 33.45));
list.add(new Student(5678, 45.45));
list.add(new Student(891, 45.45));
System.out.println("Before Sorting");
for(Object obj:list)
{
System.out.println(obj);
}
Collections.sort(list);
System.out.println("After Sorting");
for(Object obj:list)
{
System.out.println(obj);
}
System.out.println("Program ends");
}
}
class Student implements Comparable
{
int stID;
double stMarks;
public Student(int stID,double stMarks)
{
this.stID=stID;
this.stMarks=stMarks;
}
public String toString()
{
return this.stID+","+this.stMarks;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Object o) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return (this.stID-((Student)o).stID);
}
}
[/java]
If user defined class is developed and have to sort the object then it should be of comparable type class and must implement comparable interface.
In compareTo() method one can define the sorting criteria based on the field of a object.
Output:
When compile the code following is the result.
[c]
5678,45.45
891,45.5
After Sorting
891,45.5
1234,23.45
2345,33.45
5678,45.45
Program ends
[/c]
One can also use Comparator class to sort any type of collections.
 Key Points
Key Points
- Collection represents a single unit of objects.
- Java HashSet class contains unique elements only.