Introduction
Introduction
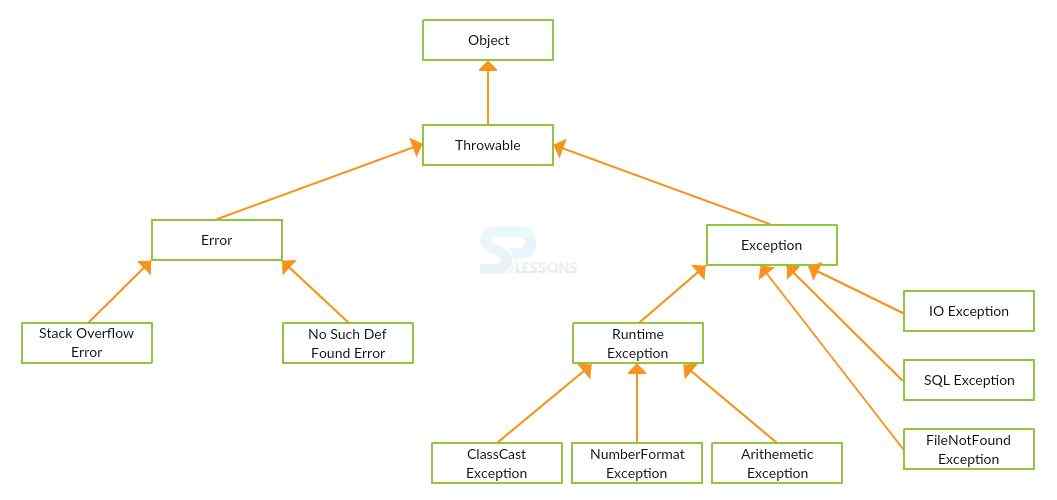
Exception Handling in Java, Exception is nothing but a bug, exception handling is the mechanism to handle the runtime errors such as ClassNotFound, IQ, SQL, Remote. Exception will be done through five keywords as follows.
1)Try
2)Catch
3)Finally
4)Throw
5)Throws
 Description
Description
Exception Handling in Java, When JVM come across an abnormal statements it creates an objects of the exception class and throws the object using “throw” keyword. The program should catch the object in order to handle it , otherwise JVM calls default handler which stops the execution. An exception can be handled by writing try-catch block. The catch block should have an argument of throwable type. If an exception occurs in a try block, the catch block statements should be executed. Following is the syntax.
[java]try
{
}
catch(Exception e)//throwable type
{
}[/java]
Exception Handling in Java, If there is no exception in try block, catch block will not be executed. For a try block, multiple catch blocks can be written. Inside try and catch block, there is a chance to write try block again. While developing try-catch block if we define multiple catch block then the catch block which is declared with super most type must be always written at the end. When it is unknown which exception will occur, then Throwable class can be used. Following is the syntax.
[java]
try
{
}
catch(ArithmeticException e1)//throwable type
{
}
catch(Exception e2)//throwable type
{
try
{
}
catch(Throwable e)//throwable type
{
}
}[/java]
Only one catch gets executed which corresponds to the execution occurred.  Description
Description
Exception Handling in Java, Finally block is used to run any mandatory statements irrespective of the occurrence of exception in the try block. The JVM runs finally block statements in all conditions except it forcefully terminated by the statement System.exit(0);. Following is the syntax.
[java]try
{
}
catch(Exception e)//throwable type
{
}
finally
{
System.out.println("Mandatory statements");
}[/java]
 Example
Example
[java]
package com.spl.exception;
public class Exception1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Program starts");
int k;
int i=10;
int j=0;
int[] array=new int[2];
System.out.println("i value="+i);
System.out.println("j value="+j);
try
{
k=i/j;
}
catch(ArithmeticException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
try
{
array[3]=456;
//System.exit(0);
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally
{
System.out.println("Running finally");
}
System.out.println("i value="+i);
System.out.println("j value="+j);
System.out.println("Program ends");
}
}
[/java]
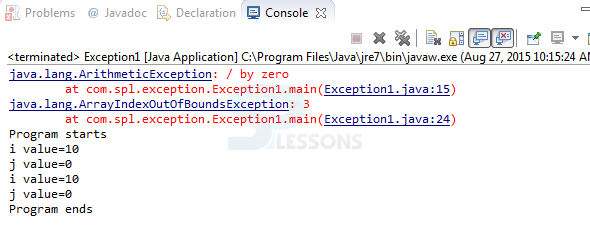
Output:
When compile the code result will be as follows.
Final is a just keyword that is used to apply restrictions on method, class and variable and final class can't be inherited, final method can't be overridden and final variable value can't be changed once it declared.
Finally is a block that is used to keep important code, it will be executed whether exception is handled or not.
Finalize is a method that is used to perform clean up processing before object is garbage colected.
 Types
Types
Exception Handling in Java, Checked Exception:During compilation if compiler checks for an occurrence of exception then it is known as checked exception. Checked exception are identified by the compiler at the time of compilation, compiler throws compile time error, stating unhandled exception. Checked exception should be handled either by try-catch block or by “throws” declaration keyword. This keyword should be used in method declaration or constructor declaration.
Unchecked Exception: Any exception if compiler is unable to identify at the time of compilation then it is known as unchecked exception. Unchecked exceptions are handled using try-catch block.
All exceptions classes inheriting Exception class, except RuntimeException are known as checked exception. Rest all are unchecked exceptions.
 More Info
More Info
An exception occurred in a method body can be handled within the method body by using try-catch block or else the object can be delegated to the caller of the method by using throws keyword. The "throws" is a declaration keyword used to throw an already created exception object to the caller of the method.
- The "throws" keyword throws checked type of exception to the caller of the method or constructor.
- Caller should either handle it or can throw the same object to its caller using throws keyword again.
- This keyword must be used only in the method as well as constructor declaration
- The called method can be handled by the thrown object by using catch-block else it can also throw object to its caller.
- Compiler will never throw an exception it just tells an error that exception is not handled.
 Syntax
Syntax
throw new ArithmeticException();
Whenever this statement is written in code, an exception by type Arithmetic Exception is thrown.One can develop user defined exception by creating a class, subclass to any of the exception type. If a subclass is created to runtime exception it will be under the category 'unchecked exception'. If a subclass is created to Exception class then it becomes 'checked exception'.  Example
Example
[java]
package com.spl.exception;
public class Exception2 {
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println("Program starts");
try
{
demo();
}
catch(ClassNotFoundException e)
{
System.out.println("Exception handled");
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Program ends");
}
static void demo() throws ClassNotFoundException
{
Class.forName("com.spl.demo");
}
}
[/java]
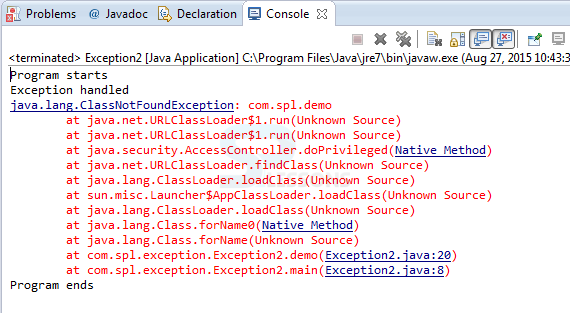
Output:
When compile the code result will be as follows.
 Example
Example
[java]
package com.spl.exception;
public class Exception3 {
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println("Program starts");
demo(12);
System.out.println("Program ends");
}
static void demo(int i)
{
if(i<15)
{
throw new ArithmeticException("i<15");
}
}
}
[/java]
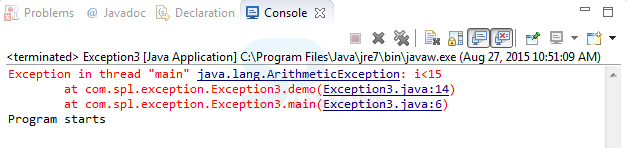
Output:
When compile the code result will be as follows.
 Key Points
Key Points
- An exception is nothing but an abnormal condition.
- The throw keyword is utilized to explicitly throw an exception.
- The throws keyword is utilized to declare an exception.