Introduction
Introduction
IBPS SO 2019 – Preliminary Examination for the posts of IT Officer (ITO), Agriculture Field Officer (AFO), HR/Personnel Officer (HRO/PO) and Marketing Officer (MO) conducted in Online Mode, has: a duration of 2 hours, a total of 150 questions, and a maximum score of 125 marks, and, consists of 3 sections, namely: English Language, Reasoning and Quantitative Aptitude. There is a Negative marking in IBPS SO Preliminary exam and 0.25 marks are deducted for each wrong answer. Candidates must clear the cut-off in all 3 sections to qualify for the IBPS SO Main exam. The below sections gives the detailed information about IBPS SO ITO AFO HRO PO MO Prelims Examination.
 Imp Dates
Imp Dates
| Event | Date |
|---|---|
| IBPS SO Notification 2019 Announcement | 05-11-2019 |
| IBPS SO Online Registration Starts From | 06-11-2019 |
| Last Date to Apply Online for IBPS SO | 26-11-2019 |
| Download of call letters for Online examination – Preliminary | 12 - 12 - 2019 |
| Closure of Call letter Download | 29-11-2019 |
| IBPS SO Preliminary Exam | [latex]{28}^{th}[/latex] and [latex]{29}^{th}[/latex] December 2019 |
| Result of IBPS SO Preliminary Exam | January 2020 |
| Download of call letters for Online examination – Mains | January 2020 |
| IBPS SO Mains Exam Date | [latex]{25}^{th}[/latex] January 2020 |
| Conduct of Interview | February 2020 |
| IBPS SO 2019-20 Final Result | April 2020 |
 Pattern
Pattern
The structure of the Examinations for the post of IT Officer, Agriculture Field Officer, HR/Personnel Officer and Marketing Officer which will be conducted online are as follows:
| SL | Name of Test | Number of Questions | Maximum Marks | Medium of Exam | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | English language | 50 | 25 | English | 40 minutes |
| 2 | Reasoning ability | 50 | 50 | English and Hindi | 40 minutes |
| 3 | Quantitative Aptitude | 50 | 50 | English and Hindi | 40 minutes |
| Total | 150 | 125 |
Note: Penalty for Wrong Answers.
There will be penalty for wrong answers marked in the Objective Tests. For each question for which a wrong answer has been given by the candidate one fourth of the marks assigned to that question will be deducted as penalty to arrive at corrected score. If a question is left blank, i.e. if no answer is marked by the candidate, there will be no penalty for that question.
 English
English
| S.No | English Language Topics |
|---|---|
| 1 | Cloze Test |
| 2 | Reading Comprehension |
| 3 | Spotting Errors |
| 4 | Sentence Improvement/Sentence Correction |
| 5 | Para Jumbles |
| 6 | Fill in the Blanks |
| 7 | Para/Sentence Completion |
Directions to Solve
Today most businessmen are very worried. To begin with, they are not used to competition.In the past they sold whatever ...(1)... produced at whatever prices they chose. But ...(2)... increasing competition, customers began to ...(3)... and choose. Imports suddenly became ...(4)... available and that too at cheaper ...(5)...
1. (Solve as per the direction given above)
- A. it
B. he
C. they
D. we
- A. with
B. by
C. after
D. from
- A. buy
B. take
C. pick
D. want
- A. hardly
B. easily
C. frequently
D. conveniently
- A. costs
B. returns
C. dividend
D. prices
Directions (1-15): Read the following passage carefully and answer the question given below it. Some words have been printed in bold to help you locate them while answering some of the questions.
In the olden days, students used to stay in the teacher’s house and learn. At a young age, boys were sent to the teacher’s house. This system of education was called ‘Gurukula’.
Prabhakaran was a boy of twelve. He was staying in his teacher’s house to learn Sanskrit. Prabhakaran was a good student and his teacher liked him. But the teacher didn’t show his affection towards the boy. Rather, he was stricter towards him. One day Prabhakaran was not very attentive in the class. This made the teacher angry. He beat him severely. Prabhakaran wept for some time. Then he wanted to wreak his vengeance on the teacher. In his rage he decided to kill the teacher. He chalked out a plan for this; Prabhakaran would climb up to the roof of his teacher’s bedroom with heavy granite stone and drop it on the teacher’s head when he was asleep. So after taking the dinner, Prabhakaran went out, picked up a heavy stone and climbed to the roof of the room. After some time his teacher and his wife retired to bed. Before sleeping they talked for some time. During the talk Prabhakaran heard his name being mentioned. He listened to their conversation attentively. The teacher’s wife was equally fond of Prabhakaran. She was telling the teacher, ‘this morning you were very harsh on Prabhakaran. You beat him umpteen times, mercilessly. Is he not the best boy in your class? If you behave in this manner he will run away from here and you will lose a good student.’
The teacher replied, ‘you are right, I should not have been so cruel to him. But you know he was not attentive in the class. I was taking an important lesson and he was talking to another boy. When I saw it I lost my temper. Prabhakaran should not miss important lessons. So I beat him in such a way that the punishment may deter him from such indifference in future.’
On hearing this, Prabhakaran became very sad. It was with good intention that the teacher punished him. He was overwhelmed with remorse. The whole night he sat on the roof. The next morning after lessons, he approached his teacher when he was alone and confessed to him everything.
1. Why did the student decide to remain on the roof whole night?
- A. He felt so guilty that he did not have courage to come down.
B. He waited for the teacher to sleep
C. He waited to hear the conversation in the teacher’s room
D. He did not know the way to come down
E. None of these
- A. To create a situation so that the teacher becomes helpless.
B. To kill the wife of the teacher
C. To peep into his bedroom from the roof top
D. To crush the teacher’s head with a stone at night
E. None of these
- A. The system of read and recite
B. The system of day and night school
C. Staying in teacher’s house and work for him
D. The Gurukula system of learning Sanskrit
E. None of these
- A. He developed hatred towards him
B. He knew that Prabhakaran was a potential killer
C. Prabhakaran did not have sympathy towards teacher’s wife
D. The teacher had seen him talking with other boys
E. None of these
- A. to reform him as he was bad in studies
B. to teach him as he was not paying attention
C. to send message to the class to improve their behavior
D. to make the boy vindictive
E. None of these
- A. Going to roof top with granite stone
B. Listening to the bedroom conversation
C. Indulging into the conversation with other boys during class
D. The weeping of Prabhakaran
E. None of these
- A. most dishonest, insincere boy
B. the best student in the class
C. a short tempered sensitive boy
D. a student who deserved much more punishment
E. a sycophant who used to praise the teacher for no reason
- A. should wait for the couple to sleep and kill them both
B. how wrong am I to kill such a nice teacher
C. I should jump onto the bed of the couple from roof top
D. Alas! I should not have heard the conversation
E. None of these
- A. The Gurukula system of education was forced on Prabhakaran
B. The teacher assaulted the student mercilessly
C. The teacher’s wife was astonished at the behavior of Prabhakaran
D. Prabhakaran did not have guilt feeling even after hearing the conversation
E. Prabhakaran had no plan to kill the teacher
- A. In old days boys at young age were sent to teacher’s house
B. But for bedroom conversation, Prabhakaran would not have killed the teacher
C. Prabhakaran was the best student in the class
D. The teacher’s wife was of the view that Prabhakaran might run away
E. The teacher was teaching an important lesson
- A. greed
B. satisfaction
C. morse
D. guilt
E. accuracy
- A. harshly
B. calmly
C. lightly
D. happily
E. accidentally
- A. tired
B. exhausted
C. fell
D. went
E. reclined
- A. twenty
B. nineteen
C. many
D. regular
E. rarely
- A. abstain
B. encourage
C. deploy
D. pull
E. stop
Directions to Solve: Read each sentence to find out whether there is any grammatical error in it. The error, if any will be in one part of the sentence. The letter of that part is the answer. If there is no error, the answer is 'D'. (Ignore the errors of punctuation, if any).
1. (Solve as per the direction given above)
- A. We discussed about the problem so thoroughly
B. on the eve of the examination
C. that I found it very easy to work it out.
D. No error.
- A. An Indian ship
B. laden with merchandise
C. got drowned in the Pacific Ocean.
D. No error.
- A. I could not put up in a hotel
B. because the boarding and lodging charges
C. were exorbitant.
D. No error.
- A. the Indian radio
B. which was previously controlled by the British rulers
C. is free now from the narrow vested interests.
D. No error.
- A. If I had known
B. this yesterday
C. I will have helped him.
D. No error.
Directions to Solve: In questions given below, a part of the sentence is bold. Below are given alternatives to the bold part which may improve the sentence. Choose the correct alternative. In case no improvement is needed, option 'D' is the answer.
1. The workers are hell bent at getting what is due to them.
A. hell bent on getting
B. hell bent for getting
C. hell bent upon getting
D. No improvement
Answer: Option C
2. When it was feared that the serfs might go too far and gain their freedom from serfdom, the protestant leaders joined the princes at crushing them.
- A. into crushing
B. in crushing
C. without crushing
D. No improvement
- A. If the room was brighter
B. If the room are brighter
C. Had the room been brighter
D. No improvement
- A. improved
B. broken
C. bettered
D. No improvement
- A. His intense desire
B. His desire for power
C. His fatal desire
D. No improvement
Choose the most logical order of sentences from among the given choices to construct a coherent paragraph.
1. 1) Despite posting healthy profits, Volkswagen shares trade at a discount to peers due to bad reputation among investors.
2) A disastrous capital hike, an expensive foray into truck business and uncertainty about the reason for a share buyback have in recent years left investors bewildered.
3) The main problem with Volkswagen is the past.
4) Many investors have been disappointed and frightened away.
5) Volkswagen shares trade at about nine times the 2002 estimated earnings, compared to BMW's 19 and are the second cheapest in the sector.
- A. 52134
B. 13425
C. 32451
D. 13524
- A. 32145
B. 43125
C. 12453
D. 45123
- A. 1324
B. 4132
C. 4213
D. 4312
Directions: Pick out the most effective word from the given words to fill in the blanks to make the sentence meaningfully complete.
1. The teacher ordered Kamal to leave the room and ______ him to return.
- A. stopped
B. refused
C. forbade
D. Challenged
Directions: four alternatives a, b, c and d given under each sentence, you are required to select most suitable alternative to fill in the blank/blanks in the sentence to make it meaningful.
1. The punch made the boxer __________ with pain.
- A. wince
B. gap
C. grumble
D. fumble
- A. vicious; condemned
B. virile; forgotten
C. virtuous; remembered
D. virulent; glorified
- A. crew
B. gang
C. fleet
D. flock
- A. complex
B. obscure
C. mingled
D. Vague
- A. crude
B. cursory
C. critical
D. curious
 Reasoning
Reasoning
| S.No | Reasoning Ability Topics |
|---|---|
| 1 | Seating Arrangements |
| 2 | Puzzles |
| 3 | Inequalities |
| 4 | Syllogism |
| 5 | Input-Output |
| 6 | Data Sufficiency |
| 7 | Blood Relations |
| 8 | Order and Ranking |
| 9 | Alphanumeric Series |
| 10 | Distance and Disrection |
| 11 | Verbal Reasoning |
1. A, P, R, X, S and Z are sitting in a row. S and Z are in the center. A and P are at the ends. R is sitting to the left of A. Who is to the right of P?
- A. A
B. X
C. S
D. Z
- A. Between B and D
B. Between B and C
C. Between E and D
D. Between C and E
- A. Bindu
B. Rani
C. Mary
D. Seema
- A. Bindu
B. Rani
C. Reeta
D. Seema
- A. Mary
B. Rani
C. Reeta
D. Bindu
Directions (Q. 1-5): Study the following information and answer the following questions:
M, N, O, P, Q, R and T seven friends working in different companies – HCL, Ranbaxy, Wipro, DLF, Reliance, Tata and Samsung. Each of them has a different car viz Wagonr, Brio, Santro, Alto, Indica, Etios and Swift, but not necessarily in the same order. R works in Wipro and drives santro car. T drives swift car and does not works in Samsung. M works in Tata and does not drive either wagonr or Brio. O drives Alto car and does not work either in Reliance or Ranbaxy. P drives Indica car and works in DLF. Q does not work in Ranbaxy. N does not drive Etios. One who drives Wagnor works in Reliance.
1. Which of the following car does Q drives?
- A. Etios
B. Brio
C. Wagonr
D. Swift
E. None of these
- A. Reliance
B. Ranbaxy
C. Samsung
D. Can’t be determined
E. None of these
- A. DLF
B. Ranbaxy
C. Samsung
D. HCL
E. None of these
- A. M
B. Q
C. T
D. N
E. P
- A. T – Swift – Samsung
B. N – Wagonr – Reliance
C. N – Wagonr – Ranbaxy
D. O – Alto – Samsung
E. None of these
Directions (Q. 1-5): In each of these questions, relationships between two elements is shown in the statements. These statements are followed by two conclusions. Read the statement and give answer:
1. Statement: P = Q, M< N, P< N, J≤ M
Conclusions:
I. P> M
II. N> J
-
A. If only conclusion I follows.
B. If only conclusion II follows
C. If either conclusion I or II follows
D. If neither conclusion I nor II follows
E. If both conclusions I and II follow.
-
A. If only conclusion I follows.
B. If only conclusion II follows
C. If either conclusion I or II follows
D. If neither conclusion I nor II follows
E. If both conclusions I and II follow.
-
A. If only conclusion I follows.
B. If only conclusion II follows
C. If either conclusion I or II follows
D. If neither conclusion I nor II follows
E. If both conclusions I and II follow.
-
A. If only conclusion I follows.
B. If only conclusion II follows
C. If either conclusion I or II follows
D. If neither conclusion I nor II follows
E. If both conclusions I and II follow.
-
A. If only conclusion I follows.
B. If only conclusion II follows
C. If either conclusion I or II follows
D. If neither conclusion I nor II follows
E. If both conclusions I and II follow.
Directions to Solve: In each of the following questions two statements are given and these statements are followed by two conclusions numbered (I) and (II). You have to take the given two statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance from commonly known facts. Read the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the two given statements, disregarding commonly known facts.
Give answer:
- A. If only (I) conclusion follows
B. If sonly (II) conclusion follows
C. If either (I) or (II) follows
D. If neither (I) nor (II) follows and
E. If both (I) and (II) follow.
- A. Only (I) conclusion follows
B. Only (II) conclusion follows
C. Either (I) or (II) follows
D. Neither (I) nor (II) follows
E. Both (I) and (II) follow
- A. Only (I) conclusion follows
B. Only (II) conclusion follows
C. Either (I) or (II) follows
D. Neither (I) nor (II) follows
E. Both (I) and (II) follow
- A. Only (I) conclusion follows
B. Only (II) conclusion follows
C. Either (I) or (II) follows
D. Neither (I) nor (II) follows
E. Both (I) and (II) follow
- A. Only (I) conclusion follows
B. Only (II) conclusion follows
C. Either (I) or (II) follows
D. Neither (I) nor (II) follows
E. Both (I) and (II) follow
- A. Only (I) conclusion follows
B. Only (II) conclusion follows
C. Either (I) or (II) follows
D. Neither (I) nor (II) follows
E. Both (I) and (II) follow
Directions (1-5): Study the given information and answer the questions:
A word and number arrangement machine when given an input line of words and numbers rearranges them following a particular rule in each step. The following is an illustration of an input and rearrangement.
Input: 19 ear 24 an 18 nose 25 our 32 mind 9 box
Step I: 10 19 ear 24 18 nose 25 our 32 mind box an
Step II: box 10 ear 24 18 nose 25 our 32 mind an 20
Step III: 26 box 10 24 18 nose our 32 mind an 20 ear
Step IV: mind 26 box 10 24 nose our 32 an 20 ear 17
Step V: 23 mind 26 box 10 our 32 an 20 ear 17 nose
Step VI: our 23 mind 26 box 10 an 20 ear 17 nose 31
And Step VI is the last step of the rearrangement of the above input.
As per the rules followed in the above steps, find out in each of the following questions the appropriate step for the given input.
Input: 17 and 32 on 12 never 29 time 7 put 4 fix
1. In which step the elements ‘32 12 time’ found in the same order?
- A. Step I
B. Step II
C. Step III
D. Step IV
E. Step VI
- A. 12
B. time
C. put
D. 4
E. and
- A. Three
B. Four
C. Five
D. Seven
E. None of these.
- A. 11 on 30 fix 8 32 time 18 and never 3 put
B. on 11 30 fix 8 32 time and 18 never 3 put
C. 11 on 30 fix 8 32 time and 18 never put 3
D. 11 on 30 fix 8 32 time and 18 never 3 put
E. None of these
- A. time
B. 11
C. on
D. and
E. None of these
Directions (1 - 5) : In each of the following questions, a question is followed by two statements numbered I and II. Read both the statements and answer accordingly.
1. How is G related to Q?
Statement I: A is son of F. H is brother of A. R is daughter of G. Q is son of B who is married to A
Statement II: C who is married to H, is mother of P. R is sister of H
-
A. If the data in statement I alone is sufficient to answer the question.
B. If the data in statement II alone is sufficient to answer the question.
C. If the data either in statement I alone or statement II alone are sufficient to answer the question.
D. If the data given in both I and II together are not sufficient to answer the question.
E. If the data in both the statements I and II together are necessary to answer the question.
-
A. If the data in statement I alone is sufficient to answer the question.
B. If the data in statement II alone is sufficient to answer the question.
C. If the data either in statement I alone or statement II alone are sufficient to answer the question.
D. If the data given in both I and II together are not sufficient to answer the question.
E. If the data in both the statements I and II together are necessary to answer the question.
-
A. If the data in statement I alone is sufficient to answer the question.
B. If the data in statement II alone is sufficient to answer the question.
C. If the data either in statement I alone or statement II alone are sufficient to answer the question.
D. If the data given in both I and II together are not sufficient to answer the question.
E. If the data in both the statements I and II together are necessary to answer the question.
-
A. If the data in statement I alone is sufficient to answer the question.
B. If the data in statement II alone is sufficient to answer the question.
C. If the data either in statement I alone or statement II alone are sufficient to answer the question.
D. If the data given in both I and II together are not sufficient to answer the question.
E. If the data in both the statements I and II together are necessary to answer the question
-
A. If the data in statement I alone is sufficient to answer the question.
B. If the data in statement II alone is sufficient to answer the question.
C. If the data either in statement I alone or statement II alone are sufficient to answer the question.
D. If the data given in both I and II together are not sufficient to answer the question.
E. If the data in both the statements I and II together are necessary to answer the question.
1. Pointing to a woman, Abhijit said, “Her granddaughter is the only daughter of my brother.” How is the woman related to Abhijit?
-
A. Sister
B. Grandmother
C. Mother-in-law
D. Mother
-
A. Paternal Grandmother
B. Paternal Grandfather
C. Maternal Grandfather
D. Maternal Grandmother
E. Data Inadequate
-
A. Only I and II follows
B. Only II and III follow
C. Only I and III follow
D. None follows
E. All follows
-
A. Son
B. Daughter
C. Either son or daughter
D. Data Inadequate
E. None of these
-
A. Niece
B. Sister
C. Daughter
D. Cannot be determined
E. None of these
1. Sam ranked ninth from the top and thirty-eighth from the bottom in a class. How many students are there in the class?
-
A. 45
B. 46
C. 47
D. 48
E. 49
-
A. 27
B. 37
C. 38
D. 39
E. 28
-
A. 40
B. 44
C. 50
D. 55
E. 58
-
A. 12
B. 13
C. 14
D. 20
E. None of these
-
A. 36
B. 37
C. 39
D. Cannot be determined
E. None of these
Directions (1 - 5): These questions are based on the following letter / number/ symbol arrangement. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow.
L F 3 # R N 8 A @ Y 4 M © W P 6 H U 9 I K 2 E
1. Which of the following is sixth to the right of the nineteenth from the right end of the above arrangement?
-
A. Y
B. M
C. 4
D. @
E. None of these
-
A. Two
B. One
C. More than three
D. Three
E. None of these
-
A. I
B. P
C. W
D. U
E. None of these
-
A. E
B. I
C. N
D. R
E. Cannot be determined
1. Directions: Each of the following questions is based on the following information:
Six flats on a floor in two rows facing North and South are allotted to P, Q, R, S, T and U.
Q gets a North facing flat and is not next to S.
S and U get diagonally opposite flats.
R next to U, gets a south facing flat and T gets North facing flat.
If the flats of P and T are interchanged then whose flat will be next to that of U?
-
A. P
B. Q
C. R
D. T
-
A. 15 m West
B. 30 m East
C. 30 m West
D. 45 m East
-
A. 1 km
B. 2 km
C. 3 km
D. 5 km
-
A. 32 m, South
B. 47 m, East
C. 42 m, North
D. 27 m, South
1. Directions: Choose the correct alternative that will continue the same pattern and replace the question mark in the given series.
120, 99, 80, 63, 48, ?
A. 35
B. 38
C. 39
D. 40
Answer: Option A
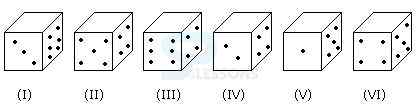
2. Directions: Six dice with upper face erased are as shown
The sum of the numbers of dots on the opposite face is 7.
If even numbered dice have even number of dots on their top faces, then what would be the total number of dots on the top faces of their dice?
-
A. 12
B. 14
C. 18
D. 24
-
A. 71 years
B. 72 years
C. 74 years
D. 77 years
-
A. 45
B. 29
C. 39
D. 37
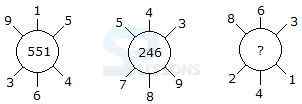
-
A. Word
B. Chorus
C. Musician
D. Tymbal
 Quantitative
Quantitative
| S.No | Quantitative Aptitude Topics |
|---|---|
| 1 | Number Series |
| 2 | Data Interpretation |
| 3 | Simplification/Approximation |
| 4 | Quadratic Equation |
| 5 | Data Sufficiency |
| 6 | Mensuration |
| 7 | Average |
| 8 | Profit and Loss |
| 9 | Ratio and Proportion |
| 10 | Time and Work |
| 11 | Time and Distance |
| 12 | Probability |
| 13 | Partnership |
| 14 | Ratio and proportion |
| 15 | Problem on Ages |
| 16 | Simple and Compound Interest |
| 17 | Permutation and Combination |
1. 26, 12, 10, 16, ?
-
A. 50
B. 52
C. 53
D. 56
E. 57
-
A. 1550
B. 1450
C. 1457
D. 1542
E. 1478
-
A. 942
B. 997
C. 919
D. 950
E. 922
-
A. 72.375
B. 84.375
C. 92.255
D. 59.750
E. 69.450
-
A. 250
B. 270
C. 260
D. 240
E. 220
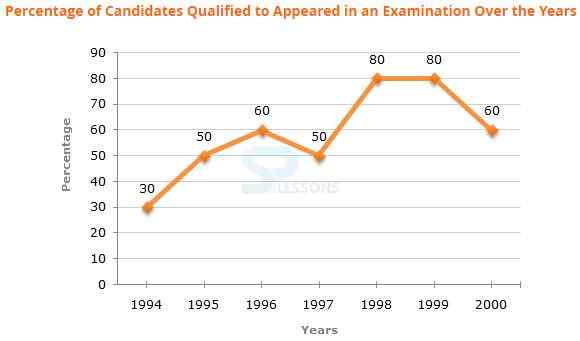
Directions(1 - 5): The following line graph gives the percentage of the number of candidates who qualified an examination out of the total number of candidates who appeared for the examination over a period of seven years from 1994 to 2000.
1. The difference between the percentage of candidates qualified to appeared was maximum in which of the following pairs of years?
A. 1994 and 1995
B. 1997 and 1998
C. 1998 and 1999
D. 1999 and 2000
Answer: Option B
2. In which pair of years was the number of candidates qualified, the same?
A. 1995 and 1997
B. 1995 and 2000
C. 1998 and 1999
D. Data inadequate
Answer: Option B
3. If the number of candidates qualified in 1998 was 21200, what was the number of candidates appeared in 1998?
A. 32000
B. 28500
C. 26500
D. 25000
Answer: Option C
4. If the total number of candidates appeared in 1996 and 1997 together was 47400, then the total number of candidates qualified in these two years together was?
A. 34700
B. 32100
C. 31500
D. Data inadequate
Answer: Option D
5. The total number of candidates qualified in 1999 and 2000 together was 33500 and the number of candidates appeared in 1999 was 26500. What was the number of candidates in 2000?
A. 24500
B. 22000
C. 20500
D. 19000
Answer: Option C
1. (4444 ÷ 40) + (645 ÷ 25) + (3991 ÷ 26) = ?
-
A. 280.4
B. 290.4
C. 295.4
D. 285.4
E. None of these
-
(a) 4.4
(b) 4
(c) 5
(d) 4.2
(e) 2.4
-
A. 56
B. 63
C. 69
D. 73
E. 82
-
A. 78
B. 92
C. 104
D. 112
E. 128
-
A. 9644
B. 11025
C. 12544
D. 13689
E. None of these
Directions(1 - 5): in each of these questions numbered I and II are given. You have to solve both the equations and Given Answer:
A. If x less than y
B. IF x less than or equal to y
C. If x greater than y
D. If x greater than or equal to y
E. If x equal to y or the relationship can’t be established
1. I. [latex]x^2[/latex] + 12x + 32 = 0
II. [latex]y^2[/latex] + 17y + 72 = 0
Answer: Option D
2. I. [latex]x^2[/latex] + 13x + 42 = 0
II. [latex]y^2[/latex] + 19y + 90 = 0
Answer: Option C
3. I. [latex]x^2[/latex] – 15x + 56 = 0
II. [latex]y^2[/latex]– 23y + 132 = 0
Answer: Option A
4. I. [latex]x^2[/latex] + 7x + 12 = 0
II. [latex]y^2[/latex] + 6y + 8 = 0
Answer: Option E
5. I. [latex]x^2[/latex] – 22x + 120 = 0
II. [latex]y^2[/latex] – 26y + 168 = 0
Answer: Option B
Directions (1 - 4): In each of the following questions, a question is followed by three statements numbered I, II and III. Read all the statements and answer accordingly.
1. What is the principal amount?
Statement I: The difference between Compound Interest and Simple Interest for 2 years is 300
Statement II: If the Compound Interest for 3 years at the rate of 10% is 3310
Statement III: If the sum becomes double in 32 years at Compound Interest?
-
A. Only I
B. Only II
C. II and III together
D. Only I or II
E. II and I or III
-
A. I and III together
B. I alone
C. I and II together
D. II and III together
E. Even all I, II, and III are not sufficient
-
A. All I, II and III
B. II alone and I and III together
C. I and II together
D. II and III alone
E. II alone
-
A. I and II Together
B. II and III Together
C. Only III
D. All I, II and III Together
E. None of these
1. The area of a rectangular plate is 236.25 sq.cm. If the length of the plate is 17.5 cm, find the perimeter of the plate.
-
A. 65 cm
B. 52 cm
C. 62 cm
D. 67 cm
E. None
-
A. 1000
B. 1200
C. 1400
D. 1800
E. None of these
-
A. 960 cm cube
B. 900cm cube
C. 1000cm cube
D. 1100 cm cube
E. None of these
-
A. 800 cm cube
B. 680 cm cube
C. 700 cm cube
D. 720 cm cube
E. None of these
-
A. 50
B. 40
C. 60
D. 55
E. None of these
1. The captain of a cricket team of 11 members is 26 years old and the wicket keeper is 3 years older. If the ages of these two are excluded, the average age of the remaining players is one year less than the average age of the whole team. What is the average age of the team?
-
A. 23 years
B. 24 years
C. 25 year
D. None of these
-
A. 3500
B. 4000
C. 4050
D. 5000
-
A. 35 years
B. 40 years
C. 50 years
D. None of these
-
A. Rs. 7.98
B. Rs. 8
C. Rs. 8.50
D. Rs. 9
-
A. 67 kg.
B. 68 kg.
C. 69 kg.
D. Data inadequate
E. None of these
Answer: Option A
1. On selling 17 balls at Rs. 720, there is a loss equal to the cost price of 5 balls. The cost price of a ball is:
-
A. Rs. 45
B. Rs. 50
C. Rs. 55
D. Rs. 60
-
A. Rs. 21,000
B. Rs. 22,500
C. Rs. 25,300
D. Rs. 25,800
-
A. 14[latex]\frac{2}{7}[/latex] % gain
B. 15% gain
C. 14[latex]\frac{2}{7}[/latex] % loss
D. 15 % loss
-
A. No profit, no loss
B. 5%
C. 8%
D. 10%
E. None of these
-
A. 12%
B. 30%
C. 50%
D. 60%
E. 1997
1. A and B together have Rs. 1210. If [latex]\frac{4}{15}[/latex] of A’s amount is equal to [latex]\frac{2}{5}[/latex] of B’s amount, how much amount does B have?
-
A. Rs. 460
B. Rs. 484
C. Rs. 550
D. Rs. 664
-
A. 2 : 5
B. 3 : 5
C. 4 : 5
D. 6 : 7
-
A. Rs. 500
B. Rs. 1500
C. Rs. 2000
D. None of these
-
A. 2 : 3 : 4
B. 6 : 7 : 8
C. 6 : 8 : 9
D. None of these
-
A. 20 litres
B. 30 litres
C. 40 litres
D. 60 litres
1. A takes twice as much time as B or thrice as much time as C to finish a piece of work. Working together, they can finish the work in 2 days. B can do the work alone in:
-
A. 4 days
B. 6 days
C. 8 days
D. 12 days
-
A. 8 days
B. 10 days
C. 12 days
D. 15 days
-
A. 18 days
B. 24 days
C. 30 days
D. 36 days
-
A. 4 days
B. 6 days
C. 8 days
D. 18 days
-
A. 3 : 4
B. 4 : 3
C. 5 : 3
D. Data inadequate
1. A person crosses a 600 m long street in 5 minutes. What is his speed in km per hour?
-
A. 3.6
B. 7.2
C. 8.4
D. 10
-
A. 300 kmph
B. 360 kmph
C. 600 kmph
D. 720 kmph
-
A. 50 km
B. 56 km
C. 70 km
D. 80 km
-
A. 100 kmph
B. 110 kmph
C. 120 kmph
D. 130 kmph
-
A. 9
B. 10
C. 12
D. 20
1. There are 100 tickets in a box numbered 1 to 100. 3 tickets are drawn at one by one. Find the probability that the sum of number on the tickets is odd.
-
A) 2/7
B) 1/2
C) 1/3
D) 2/5
E) 3/7
-
A) 85/216
B) 34/75
C) 95/216
D) 35/72
E) 13/36
-
A) 85/99
B) 81/93
C) 83/99
D) 82/93
E) 84/99
-
A) 1/9
B) 3/10
C) 4/15
D) 1/10
E) 5/12
-
A) 8/15
B) 5/16
C) 7/15
D) 3/10
E) 13/21
1. Antra and Manvi invested Rs 3780 and Rs 3960 in a business. After 3 months, Antra withdew Rs 420 and Manvi withdrew Rs 180. At the same time Chetna joined them by investing Rs 4620. After a year, they made a profit of Rs 35,850. Find Manvi’s share in the annual profit.
-
A) Rs 13,450
B) Rs 12,750
C) Rs 12,350
D) Rs 13,650
E) Rs 13,950
-
A) Rs 7570
B) Rs 6400
C) Rs 7560
D) Rs 7150
E) Rs 8180
-
A) Rs 17,000
B) Rs 25,000
C) Rs 18,000
D) Rs 12,000
E) Rs 27,000
-
A) Rs 2700
B) Rs 1900
C) Rs 2100
D) Rs 2400
E) Rs 1600
-
A) Rs 12375
B) Rs 13455
C) Rs 14265
D) Rs 14350
E) Rs 12225
1. The present ages of three persons in proportions 4 : 7 : 9. Eight years ago, the sum of their ages was 56. Find their present ages (in years).
-
A. 8, 20, 28
B. 16, 28, 36
C. 20, 35, 45
D. None of these
-
A. 2 years
B. 4 years
C. 6 years
D. 8 years
-
A. 32 years
B. 36 years
C. 40 years
D. 48 years
-
A. 1 year
B. 2 years
C. 25 years
D. cannot be determined
-
A. 5 : 2
B. 7 : 3
C. 9 : 2
D. 13 : 4
1. Out of a sum of Rs 850, a part was lent at 6% SI and the other at 12% SI. If the interest on the first part after 2 years is equal to the interest on the second part after 4 years, then the second sum is
-
A) Rs350
B) Rs280
C) Rs170
D) Rs220
E) None
-
A) Rs850, 10%
B) Rs900, 12%
C) Rs800, 13%
D) Rs1000,15%
E) None
-
A) Rs1800
B) Rs1750
C) Rs2000
D) Rs1655
E) None
-
A) Rs1230
B) Rs1135
C) Rs1080
D) Rs1100
E) None
1. In how many ways can a group of 5 men and 2 women be made out of a total of 7 men and 3 women?
-
A. 63
B. 90
C. 126
D. 45
E. 135
-
A. 40
B. 400
C. 5040
D. 2520
-
A. 10080
B. 4989600
C. 120960
D. None of these
-
A. 120
B. 720
C. 4320
D. 2160
E. None of these