Introduction
Introduction
Storage devices are any type of hardware that is capable of storing and retrieving data. Most often these devices come in the form of hard drives or optical discs. There are two main categories of storage devices. Primary storage, such as RAM, is used by computer systems to temporarily store and retrieve data. Secondary storage devices, such as hard drives stores data permanently.
 Concepts
Concepts
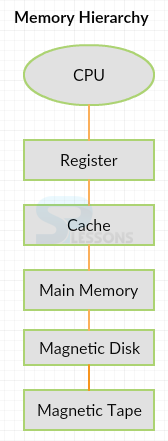
- Register can set flip- flops. These are very close to the CPU. The register is the fastest memory.
- Cache memory can store important data, i.e., highly executed data. It is the fast and smallest memory.
- It stores the data for immediate manipulations.
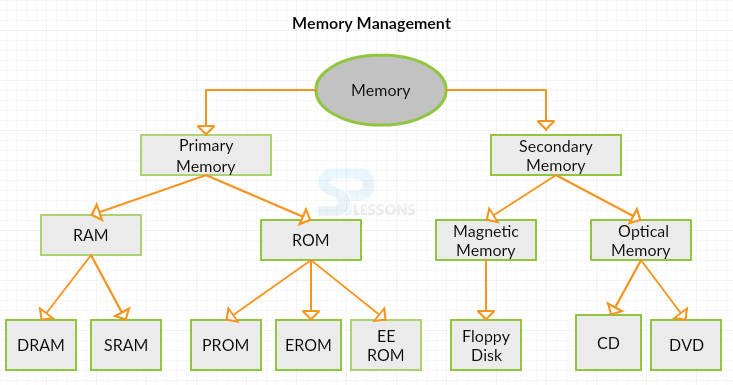
- Primary memory
- Secondary memory
- DRAM
- SRAM
- DRDRAM
- DRAM is less expensive to produce than other RAMs
- DRAM writes data at the byte-level and reads at the multiple-byte page level
- DRAM requires less power than other RAMs
- Static RAM
- Static RAM provides faster access to data and is more expensive than DRAM
- It is an expensive memory in which each cell must contain multiple transistors.
- Static RAM does not use capacitors. The cache memory is implemented in the cache memory. It is an expensive memory in which each cell must contain multiple transistors.
- SRAM is also highly recommended for use in PCs, peripheral equipment, printers, LCD screens, hard disk buffers, router buffers and buffers in CDROM / CDRW drives.
- It is used in Video game consoles because its transfer rate of data is high compared all types of RAMs.
- RDRAM densities are 128 Mbit and 256 Mbit.
- PROM
- EPROM
- EEPROM - Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory
- Flash EEPROM memory
- It is used in digital electronic devices to store permanent data.
- It is available in low cost as compared to other RAMs.
- In EPROM we need to erase each and every cell.
- We can’t erase data in RAM, PROM only we can erase data in EPROM.
- EEPROM requires data to be written or erased one byte at a time
- EEPROM are used to store configurations parameters and in modern computers, they replaced BIOS CMOS memory.
- It is more expensive than other hard drives and RAMSs.
- It can be erased only limited number of times
| Secondary Memory Device | Storage | Capacity |
|---|---|---|
| Floppy Disk (5.25 inches) | Magnetic | 1.2 MB |
| Floppy Disk (3.5 inches) | Magnetic | 1.44 MB |
| Floppy Disk (3.55 inches) | Magnetic | 80 KB to 242 KB |
| Hard Disk | Magnetic | upto 1 TB |
| CD-ROM | Optical | 640 MB to 680 MB |
| DVD-ROM | Optical | 4.7 GB to 17 GB |
| Pen-Drive | Solid State | 1 GB to 512 GB |
| Magnetic tape | Magnetic | Upto 1 TB |
- A Bit is a single binary value that may be 0 or 1.
- A Nibble is a group of 4 bits.
- A Byte is a group of 8 bits and is equal to one character.
| Name | Size |
|---|---|
| 1 bit | Single digit 0 or 1 |
| 1 nibble | 4 bits |
| 1 byte | 8 bits |
| 1 Kilobyte(KB) | 1024 Bytes |
| 1 Megabyte(MB) | 1024 KB |
| 1 Gigabyte(GB) | 1,024 MB |
| 1 Terabyte(TB) | 1,024 GB |
| 1 Petabyte (PB) | 1,024 TB |
| 1 Exabyte (EB) | 1,024 PB |
| 1 Zetta byte (ZB) | 1,024 EB |
| 1 Yotta Byte (YB) | 1,024 ZB |
| 1 Bronto Byte | 1,024 YB |
| 1 Geop Byte | 1,024 Bronto Byte |
 Questions
Questions
1. The full form of PB____.
- Penta Byte
- Platter Byte
- Plane Bits
- Penta Bits
- Optical disk
- Magnetic disk
- Magnetic tape
- Pen drive
- Bit
- Byte
- Zetta
- GEOP
- KB
- GB
- MB
- ZB
- Tracking
- Allotting
- Crashing
- Formatting
- Floppy
- Permanent Disk
- Optical Disk
- Hard Disk
- FLOPPY Disk
- ZIP Disk
- Hard Disk
- CD
- 80KB to 242 KB
- 120KB to 240 KB
- 70KB to 160 KB
- 180KB to 242 KB
- Hard disk
- Output device
- Solid state storage device
- Optical disk
- Steel
- Magnetic
- Optical
- Flash
- Folder
- Network
- Sub
- Root
- Propagation
- Magnetization
- Centrifugation
- Gravitation
- Diskette/CD’s
- Hard disk
- System cabinet
- Main memory
- CAM
- The DVD/BD
- The hard disk
- Emulation
- Magnetic tape
- Floppy disk
- Compact disk
- All of the above