Description
Description
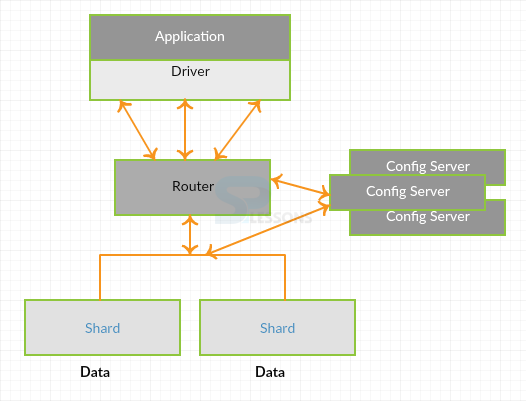
MongoDB Sharding is a technique of accumulating informational records over numerous apparatus and MongoDB's computation that deal with handling the requests regarding the information development. As there is an increment in the data size, a solitary apparatus may not be adequate to store the information nor give a adequate compose and read throughput. MongoDB Sharding determine the issue including scaling that are horizontal. MongoDB Sharding apparatus to bolster information development and the requests for compose and read functions.
 Description
Description
There are two types of MongoDB Sharding as follows.
- Horizontal
- Vertical
 Description
Description
Horizontal Scaling includes isolating the framework dataset and load over numerous servers, additional servers to increase capacity as required. While the general velocity or limit of a solitary machine may not be high, every machine handles a subset of the general workload, possibly giving preferred effectiveness over a solitary rapid high-limit server. Expanding the limit of the organization just requires including extra servers as required, which can be a lower general expense than top of the line equipment for a solitary machine. The exchange off is expanded intricacy in infrastructure and maintenance for the arrangement.
 Description
Description
Vertical Scaling includes expanding the limit of a solitary server, for example, utilizing an intense CPU, including more RAM, or expanding the measure of storage space. Impediments in accessible innovation may limit a solitary machine from being adequately capable for a given workload. Moreover, Cloud-based suppliers have hard roofs in view of accessible equipment setups. Subsequently, there is a practical maximum for vertical scaling.
 Description
Description
- In replication containing each and every composes for skilled growth.
- Dormancy delicate inquiries still go to skilled.
- Solidarity replication set have restriction of node number of 12.
- Memory cannot be sufficiently substantial when dynamic set of data is enormous.
- Residing Disk is not sufficiently enormous.
- Vertical scaling is excessively costly.
 Key Points
Key Points
- MongoDB Sharding - Accumulating informational records.