Introduction
Introduction
NEET 2020 Medical Entrance Exam for All India MBBS/BDS Seats. NEET is one of the toughest medical entrance exams in India. It will be conducted by NTA on 03rd May 2020. The Government of India has made the National Eligibility cum Entrance Test the only exam to pursue medical courses abroad and India.It is divided into three parts Physics, Chemistry and Biology (Botany & Zoology). The exam is conducted in offline mode only. Once check the sample questions related to NEET Physics section.
 Pattern
Pattern
| Section | No. of Question | Maximum Marks |
|---|---|---|
| Physics | 45 | 180 |
| Chemistry | 45 | 180 |
| Botany | 45 | 180 |
| Zoology | 45 | 180 |
| Total | 180 | 720 |
Note: In NEET Exam Pattern 2020, the stationary and all the other required material will be provided to candidates inside the examination hall only.
- Total 180 questions are assigned to Physics, Chemistry & Biology (Botany and Zoology) The Question Paper carries 720 marks,.For each correct answer, 4 marks will be awarded.
- 1 mark will be deducted for every incorrect answer.
- Remember that once you filled the registration form and submitted, the language of the paper cannot be changed.
- As per the NEET Exam Pattern 2020, candidates who choose the English language will get the Question Paper booklet in English only.
- Those candidates who choose the Hindi language will get a bilingual booklet in English and Hindi.
 Syllabus
Syllabus
NEET Syllabus - Physics
[/accordion_tab][/accordion_tabs]
| S. No. | CLASS XI | CLASS XII |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Physical world and measurement | Electrostatics |
| 2. | Kinematics | Current Electricity |
| 3. | Laws of Motion | Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism |
| 4. | Work, Energy and Power | Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents |
| 5. | Motion of System of Particles and Rigid Body | Electromagnetic Waves |
| 6. | Gravitation | Optics |
| 7. | Properties of Bulk Matter | Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation |
| 8. | Thermodynamics | Atoms and Nuclei |
| 9. | Behaviour of Perfect Gas and Kinetic Theory | Electronic Devices |
| 10. | Oscillations and Waves |
 Weightage
Weightage
NEET Chapter WISE WEIGHTAGE for Physics
| Physics Chapters and topics | Average no. of Questions from the chapter | Weightage of the chapter and topic (In percentage) |
|---|---|---|
| Centre of Mass | 1 | 1% |
| Gravitation | 2 | 3% |
| Kinematics | 1 | 2% |
| Laws of Motion | 3 | 7% |
| Mechanics of Solids & Fluids | 2 | 3% |
| Oscillations | 1 | 3% |
| Rotational motion | 1 | 1% |
| System of Particle & Rigid Body | 3 | 7% |
| Units and Measurement | 1 | 2% |
| Waves | 2 | 4% |
| Work, Energy and power | 2 | 4% |
| Kinetic Theory of Gases | 1 | 2% |
| Properties of Bulk Matter | 1 | 3% |
| Thermal Properties of Matter | 1 | 2% |
| Thermodynamics | 3 | 7% |
| Magnetic Effect of Current & Magnetism | 3 | 6% |
| Electric Charge & Field | 1 | 2% |
| Electromagnetic Wave | 1 | 1% |
| Electrostatic Potential & Capacitance | 1 | 2% |
| Electrostatics | 1 | 3% |
| Alternating Current | 1 | 3% |
| Current Electricity | 3 | 6% |
| Electromagnetic Induction | 1 | 2% |
| Semiconductor Electronics | 3 | 6% |
| Atoms & Nuclei | 1 | 5% |
| Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter | 2 | 4% |
| Ray Optics & Optical Instrument | 3 | 5% |
| Wave optics | 2 | 4% |
 Resources
Resources
 Class - XI
Class - XI
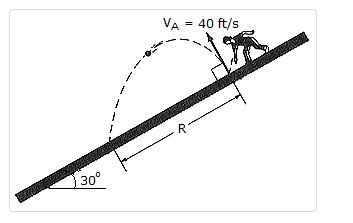
1. A ball is thrown downward on the 30° inclined plane so that when it rebounds perpendicular to the incline it has a velocity of vA = 40 ft/s. Determine the distance R where it strikes the plane at B.
- A. R = 66.3 ft
B. R = 99.4 ft
C. R = 172.1 ft
D. R = 344 ft
- A. a = 0.617 m/[latex]{s}^{2}[/latex]
B. a = 1.037 m/[latex]{s}^{2}[/latex]
C. a = 1.451 m/[latex]{s}^{2}[/latex]
D. a = 0.833 m/[latex]{s}^{2}[/latex]
- A. t = 8 s, s = 800 ft
B. t = 8 s, s = 320 ft
C. t = 4 s, s = 240 ft
D. t = 4 s, s = 40
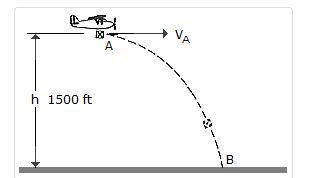
- A. p2 = 9860 ft
B. p2 = 3000 ft
C. p2 = 1500 ft
D. p2 = 8510 ft
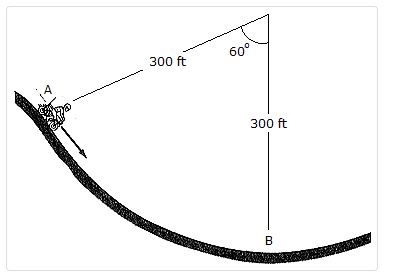
- A.v = 51.1 ft/, a[latex]{s}^{2}[/latex] = 9.83 ft/[latex]{s}^{2}[/latex]
B.v = 51.1 ft/[latex]{s}^{2}[/latex], a = 8.18 ft/[latex]{s}^{2}[/latex]
C.v = 51.1 ft/[latex]{s}^{2}[/latex], a = 10.31 ft/[latex]{s}^{2}[/latex]
D.v = 51.1 ft/[latex]{s}^{2}[/latex], a = 8.69 ft/[latex]{s}^{2}[/latex]
1. An electron and a proton are moving under the influence of mutual forces. In calculating the change in the kinetic energy of the system during motion, one ignores the magnetic force of one on another.
This is because.
- A.the two magnetic forces are equal and opposite, so they produce no net effect.
B.the magnetic forces do no work on each particle.
C.the magnetic forces do equal and opposite (but non-zero) work on each particle.
D.the magenetic forces are necessarily negligible.
- A. same as the same force law is involved in the two experiments.
B. less for the case of a positron, as the positron moves away more rapidly and the force on it weakens.
C. more for the case of a positron, as the positron moves away a larger distance.
D. same as the work done by charged particle on the stationary proton
- A. constant and equal to mg in magnitude.
B. constant and greater than mg in magnitude.
C. variable but always greater than mg.
D. at first greater than mg, and later becomes equal to mg.
- A. + 2000J
B. – 200J
C. zero
D. – 20,000J
- A. Kinetic energy.
B. Potential energy.
C. Total mechanical energy.
D. Total linear momentum.
1. A ball is travelling with uniform translatory motion. This means that
- A. it is at rest.
B. the path can be a straight line or circular and the ball travels with uniform speed.
C. all parts of the ball have the same velocity (magnitude and direction) and the velocity is constant.
D. the centre of the ball moves with constant velocity and the ball spins about its centre uniformly.
- A. the force acting on the scale is zero, but a torque about the centre of mass can act on the scale.
B. the force acting on the scale is zero and the torque acting about centre of mass of the scale is also zero.
C. the total force acting on it need not be zero but the torque on it is zero
D. neither the force nor the torque need to be zero.
- A. conservation of energy.
B. Newton’s first law only.
C. Newton’s second law only.
D. both Newton’s second and third law.
- A. frictional force along westward
B. muscle force along southward.
C. frictional force along south-west.
D. muscle force along south-west.
- A.136 N
B.134 N
C.158 N
D.68 N
1. Unit of reduction factor is
- A.ampere
B.ohm
C.tesla
D. weber
- A. independent of unit
B. directly proportional to unit
C. inversely proportional to unit
D. directly proportional to the square root of the unit
- A. illuminating power
B. luminous flux
C. luminous intensity
D. None of these
- A. spring constant
B. surface energy
C. surface energy
D. acceleration due to gravity
- A. Displacement
B. Angle
C. Couple
D. Speed
1. By what percentage does the kinetic energy increase, if the linear momentum is increased by 50%
- A. 25%
B. 50%
C.100%
D. 125%
- A. The vector is perpendicular to the orbital plane
B. The vector is along the radius vector
C. The vector is parallel to the linear momentum
D. The vector is in the orbital plane
- A. Axis of rotation
B. Angular velocity
C.Distribution of mass
D. Mass of an object
- A. There is a decrease in the rotational motion
B. There is a decrease in the rotational and transnational motion
C. There is a conversion of transnational motion into rotational motion
D. Kinetic energy is converted into heat
- A. When the motion is rotational
B.When the motion is linear
C.When the motion is along a curved path
D. None of the above
1. The earth is an approximate sphere. If the interior contained matter which is not of the same density everywhere, then on the surface of the earth, the acceleration due to gravity
- A. will be directed towards the centre but not the same everywhere.
B. will have the same value everywhere but not directed towards the centre.
C. will be same everywhere in magnitude directed towards the centre.
D. cannot be zero at any point
- A. be similarly true
B. not be true because the force between earth and mercury is not inverse square law.
C. not be true because the major gravitational force on mercury is due to sun.
D. not be true because mercury is influenced by forces other than gravitational forces.
- A. the torque is zero.
B. the torque causes the earth to spin.
C. the rigid body result is not applicable since the earth is not even approximately a rigid body.
D. the torque causes the earth to move around the sun.
- A. the solar cells and batteries in satellites run out.
B. the laws of gravitation predict a trajectory spiraling inwards.
C. of viscous forces causing the speed of satellite and hence height to gradually decrease.
D. of collisions with other satellites.
- A. will be elliptical.
B. will not be strictly elliptical because the total gravitational force on it is not central.
C. is not elliptical but will necessarily be a closed curve.
D. deviates considerably from being elliptical due to influence of planets other than earth.
1. Modulus of rigidity of ideal liquids is
- A. infinity
B. zero
C. unity
D. some finite small non-zero constant value.
- A. be double
B. be half.
C. be four times.
D. remain same.
- A.will also double
B.will become four times.
C.will remain same.
D.will decrease
- A. volumetric.
B. shear
C. longitudinal and shear.
D.longitudinal.
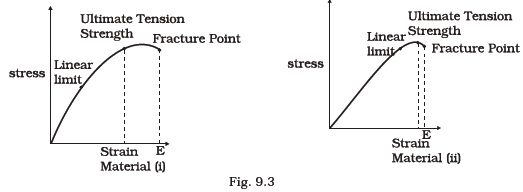
- A. Material (ii) is more elastic than material (i) and hence material (ii) is more brittle.
B. Material (i) and (ii) have the same elasticity and the same brittleness.
C. Material (ii) is elastic over a larger region of strain as compared to (i).
D. Material (ii) is more brittle than material (i).
1. The energy required to increase the temperature of one pound of water one degree Fahrenheit is known as a Btu. For what does this abbreviation stand?
- A.Big Temperature Unit
B.Brenwald’s Thermal Unit
C.Britain Temperature Unification
D.British Thermal Unit
- A.Enthalpy
B.Chaos
C.Entropy
D.Disequilibrium
- A. 100 J
B. 99 J
C. 90 J
D. 1 J
- A. Compressing the gas isothermally or adiabatic ally will require the same amount of work
B. Which of the case (whether compression through isotherm or through adiabatic process) requires more work will depend upon the atomicity of the gas
C. Compressing the gas isothermally will require more work to be done
D. Compressing the gas through adiabatic process will require more work to be done
- A. Isothermal
B. Adiabatic
C. Isobaric
D. Isochoric
1. On which factor does the average kinetic energy of gas molecules depend?
- A. Nature of the gas
B. Temperature
C. Volume
D. Mass
- A. Infinity
B. Constant
C. Unstable
D. Zero
- A. Increase
B. Decrease
C. Remain the same
D. Decreases for some, while the increase for others
- A. Joule’s effect is positive
B. Van der Waal’s equation becomes zero
C. Gases obey Boyle’s law
D. Water solidifies
- A. Strike the walls with higher velocities
B. Strike the walls with large farce
C. Strike the walls more frequently
D. Are in contact with the walls for a shorter time
1. A linear harmonic oscillator of force constant 2×106 N/m and amplitude 0.01m has a total mechanical energy of 160J. Its ___________
Explanation: Potential energy = 1/2×kx2
= [latex]\frac{1}{2}[/latex] × 2 × 106 × 0.012 = 100J.
- A. Potential energy is 160 J
B. Potential energy is zero
C. Potential energy is 100J
D. Potential energy is 120J
- A. [latex]\frac{A}{4}[/latex]
B. [latex]\frac{A}{2}[/latex]
C. 3[latex]\frac{A}{4}[/latex]
D. Some other fraction of A
- A. 8 sec
B.12 sec
C.16 sec
D.4 sec
- A. Moving down with uniform acceleration
B.b) Moving around the earth in geostationary orbit
C. Moving up with uniform velocity
D. Moving up with uniform acceleration
- A. Circle
B. Figure of eight
C. Straight line
D. Ellipse
 Class-XII
Class-XII
1. What are the basic components of simple electric current?
- A.energy source
B.connecting wires
C. switch
D. All the above
- A. Voltage
B. Current
C. Electric Force
D.Movement of Protons
- A. insulators
B. conductors
C. semi conductors
D.None of the above
- A. galvanometer
B. ammeter
C. voltmeter
D.poteintmeter
- A.electric potential
B.electric resistance
C. electric current
D.None of the above
1. As per Coulomb’s law, the force of attraction or repulsion between two point charges is directly proportional to the
- A. sum of the magnitude of charges
B. product of the magnitude of charges
C. square of the distance between them
D. cube of the distance
- A. Magnitude of the charge enclosed by the surface.
B. Position of the charge enclosed by the surface
C. The shape of the surface
D. None of these
- A. Copper
B. Silver
C. Glass
D. Aluminum
- A. Electric current
B. Electric field intensity
C. Electric potential
D. Electric flux
- A. V-m
B. N—C/m
C. V/m
D. N—C
1. Who discovered the magnetic field of current?
- A. William Gilbert
B. Hans Christian Oersted
C. Benjamin Franklin
D. Charles Augustin de Coulomb
- A. Mechanical
B. Friction
C. Spring
D. Gravitational
- A. The presence of metal
B. Current flowing in it
C. Circular loop
D. No current in it
- A. Electric motor
B. Telephone
C. Radio
D. All of the above
- A. Bigger circles
B. Straight
C. Concentrated circles
D. Parallel straight
1. What happens to the current in a coil while accelerating a magnet inside it?
- A.Increases
B. Decreases
C. Remains constant
D. Reverses
- A.Current
B.Voltage
C.Electromagnetic induction
D.EMF
- A. 0.3V
B. 0.03V
C. 30V
D. 3V
- A. Change in the magnetic field only
B. Change in the area of cross section only
C. Change in angle between magnetic field and area only
D. Change in the magnetic field, area or angle between them
- A. Voltage
B. EMF
C. Magnetic flux
D. Magnetic flux density
1. Arrange the following electromagnetic radiations per quantum in the order of increasing energy:
A : Blue light
B : Yellow light
C : X-ray
D : Radiowave
- A. A, B, D, C
B. C, A, B, D
C. B, A, D, C
D. D, B, A, C
- A.A changeless particle
B. An accelerating charge
C.A charge moving at constant velocity
D.A stationary charge
- A. 1.73 V/m
B. 2.45 V/m
C. 5.48 V/m
D. 7.75 V/m
- A. in opposite phase and perpendicular to each other
B.in opposite phase and parallel to each other
C.in phase and perpendicular to each other
D. in phase and parallel to each other
- A. in mutually perpendicular planes but vibrating with a phase difference of π
B.in mutually perpendicular planes but vibrating with a phase difference of π/2
C.in randomly oriented planes but vibrating in phase
D. in mutually perpendicular planes but vibrating in phase
1. The direction of propagation of an electromagnetic wave is the same as:
- A.E
B.E.B
C.E×B
D.B×E
- A. Propagation in media depends on re-radiation by electron-oscillators, which takes a finite time to occur.
B. Electron oscillators in the medium introduce a phase change upon re-radiation.
C. A medium is a different reference frame to vacuum, so the difference in the observed speed of light is a consequence of relativity.
D. Light is slowed down because it does not take a straight line path through the dense medium
- A. I only.
B. I and II.
C. II and III.
D. II only.
- A.Much more red light than blue light is absorbed by air atoms.
B.Red light is reflected by the atmosphere.
C. Blue light is scattered to a greater extent than red light.
D.Higher energy light waves have more penetration through the atmosphere.
- A. aμ1 + b
B. a2bμ2
C. – μ1.
D. aμ1μ2
1.Energy produced in sun is due to .
3. The quantity which is not conserved in a nuclear reaction is
- A. Motion of electrons and ion
B.Chemical reaction
C.Fusion reaction
D. Fission reaction
- A. increases
B. decreases
C. remains unchanged.
D. may increase or decrease depending upon the nucleus.
3. The quantity which is not conserved in a nuclear reaction is
- A. momentum
B.charge
C.mass
D. none of these
- A. isotopes
B. isotones
C. isomers
D. isobars
- A. 27
B. 40
C. 56
D. 120
1.Two semiconductor material have exactly the same properties except that material A has a bandgap of 1.0 eV and material B has a bandgap energy of 1.2 eV. The ratio of intrinsic concentration of material A to that of material B is
- A. 2016
B. 47.5
C. 58.23
D. 1048
- A. 300 K
B. 360 K
C. 382 K
D. 364 K
- A. 150V
B. 100V
C. 300V
D. 400V
- A. 1.9 eV
B. 1.3 eV
C. 2.6 eV
D.2.6 eV
- A.26.8
B. 18.4
C.8.5
D. 3.6