Introduction
Introduction
Matter is defined as anything that occupies space and has mass. Fact: All matter has physical and chemical properties. Properties of Matter Quiz lists some important questions for competitive exams related to the study of Physical and Chemical Properties.
What are Physical Properties? Physical properties are characteristics can be measured without changing the composition of the sample under study, such as mass, color, and volume (the amount of space occupied by a sample).
What are Chemical Properties? Chemical properties describe the characteristic ability of a substance to react to form new substances; they include its flammability and susceptibility to corrosion. Chemical properties deal with how one chemical reacts with another. Fact: All samples of a pure substance have the same chemical and physical properties. Example: Pure copper is always a reddish-brown solid (a physical property) and always dissolves in dilute nitric acid to produce a blue solution and a brown gas (a chemical property). Wood is recorded as flammable because it becomes heat, ash, and carbon dioxide when heated in the presence of oxygen.
Extensive vs. Intensive Properties: Physical properties can be extensive or intensive. Extensive properties vary with the amount of the substance and include mass, weight, and volume. Intensive properties, on the other hand, do not depend on the amount of the substance; they include color, melting point, boiling point, electrical conductivity, and physical state at a given temperature. For example, elemental sulfur is a yellow crystalline solid that does not conduct electricity and has a melting point of 115.2 °C, regardless of the amount that is examined. Intensive properties are primarily measured to determine a substance’s identity, and extensive properties convey information about the amount of the substance in a sample.
In simple terms, Intensive properties do not depend on the amount of matter. Example: boiling point and color and Extensive properties depend on the amount of matter that is being measured. Example: mass and volume.
 Quiz
Quiz
1. Kerosene oil rises up in a wick of a lantern because of
(a) diffusion of the oil through the wick
(b) surface tension
(c) buoyant force of air
(d) the gravitational pull of the wick
Ans: B
2. Two pieces of metal when immersed in a liquid have equal upthrust on them; then
(a) both pieces must have equal weights
(b) both pieces must have equal densities
(c) both pieces must have equal volumes
(d) both are floating to the same depth
Ans: C
3. If the force on the surface is doubled and area is reduced to half, pressure will
(a) become 2 times
(b) become 3 times
(c) become 4 times
(d) remain unchanged
Ans: C
4. Pressure at a point inside a liquid does not depend on
(a) the depth of the point below the surface of the liquid
(b) the nature of the liquid
(c) the acceleration due to gravity at that point
(d) the shape of the containing vessel
Ans: D
5. The bulk modulus for an incompressible liquid is
(a) zero
(b) unity
(c) infinity
(d) between 0 and 1
Ans: C
6. An egg when placed in ordinary water sinks but floats when placed in brine. This is because
(a) density of brine is less than that of ordinary water
(b) density of brine is equal to that of ordinary water
(c) density of brine is greater than that of ordinary water
(d) None of these
Ans: C
7. Water is flowing through a horizontal pipe in streamline flow. At the narrowest part of the pipe
(a) Velocity is maximum and pressure is minimum
(b) Pressure is maximum and velocity is minimum
(c) Both the pressure and velocity are maximum
(d) Both the velocity and pressure are minimum
Ans: A
8. The following four wires are made of the same material.
Which of these will have the largest extension when the same tension is applied ?
(a) Length = 50 cm , diameter = 0.5 mm
(b) Length = 100 cm, diameter = 1 mm
(c) Length = 200 cm, diameter = 2 mm
(d) Length = 300 cm, diameter = 3 mm
Ans: A
9. A man is sitting in a boat which is floating in pond. If the man drinks some water from the pond, the level of water in the pond will
(a) rise a little
(b) fall a little
(c) remain stationary
(d) None of these
Ans: C
10. In solids, interatomic forces are
(a) totally repulsive
(b) totally attractive
(c) combination of (a) and (b)
(d) None of the
Ans: C
11. A body floats in a liquid containing in a beaker. The whole system as shown in Fig. is falling under gravity. The upthrust on the body due to liquid is
(a) zero
(b) equal to weight of body in air
(c) equal to weight of liquid displaced
(d) equal to weight of immersed part of the body
Ans: A
12. A water tank of height 10 m, completely filled with water is placed on a level ground. It has two holes one at 3 m and the other at 7 m from its base. The water ejecting from
(a) both the holes will fall at the same spot
(b) upper hole will fall farther than that from the lower hole
(c) upper hole will fall closer than that from the lower hole
(d) more information is required
Ans: A
13. The lift of an air plane is based on
(a) Torricelli’s theorem
(b) bernoulli’s theorem
(c) law of gravitation
(d) conservation of linear momentum
Ans: B
14. The rain drops falling from the sky neither injure us nor make holes on the ground because they move with
(a) constant acceleration
(b) variable acceleration
(c) variable speed
(d) constant terminal velocity
Ans: B
15. Two soap bubbles are held by a tube. What will happen ?
(a) Air will travel from bigger to smaller bubble
(b) Air will not travel
(c) Air will travel through tube
(d) Nothing can be said
Ans: A
16. With the increase of temperature, the surface tension of the liquid
(a) may increase or decrease depending on the density of liquid
(b) remains the same
(c) always increases
(d) always decreases
Ans: D
17. According to Hooke’s law of elasticity, if stress is increased, then the ratio of stress to strain
(a) becomes zero
(b) remains constant
(c) decreases
(d) increases
Ans: B
18. Liquid pressure at a point in a liquid does not depend on the
(a) density of liquid
(b) shape of the vessel in which the liquid is kept
(c) depth of the point from the surface
(d) acceleration due to gravity
Ans: B
19. A container partly filled in a liquid is suspended from a spring balance. A small body is gently dropped in the container. The pointer of spring balance will
(a) read less
(b) oscillate
(c) read the same
(d) read more
Ans: D
20. Small droplets of a liquid are usually more spherical in shape than larger drops of the same liquid because
(a) force of surface tension is equal and opposite to the force of gravity
(b) force of surface tension predominates the force of gravity
(c) force of gravity predominates the force of surface tension
(d) force of gravity and force of surface tension act in the same direction and are equal
Ans: B
21. Which of the following materials is most elastic ?
(a) Rubber
(b) Lead
(c) Wood
(d) Steel
Ans: D
22. A stretched rubber has
(a) increased kinetic energy
(b) increased potential energy
(c) decreased kinetic energy
(d) decreased potential energy
Ans: B
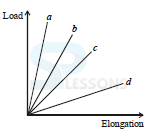
23. The load verses elongation graph for four wires is shown. The thinnest wire is
(a) a
(b) b
(c) c
(d) d
Ans: B
24. Elastomers are the materials which
(a) are not elastic at all
(b) have very small elastic range
(c) do not obey Hooke’s law
(d) None of these
Ans: C
25. The lift in an aeroplane is based on
(a) Law of gravitation
(b) Theorem of continuity
(c) Pascal’s low
(d) Bernoulli’s theorem
Ans: D
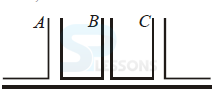
26. In the figure below is shown the flow of the liquid through a horizontal pipe. Three tubes A, B, and C are connected to the pipe. The radii of the tubes A, B and C at the junction are respectively 2 cm, 1 cm and 2 cms. It can be said that
(a) the height of the liquid in the tube A is maximum
(b) height of the liquid in the tube A and tube B is the same
(c) height of the liquid in all the three tubes is the same
(d) height of the liquid in tube A and C is the sam
Ans: D
27. Houses far from the municipal water tank find it difficult to get water on the top floor even if their ceilings are lower than the level of water filled in tank. Its reason is
(a) pipes are more wide.
(b) pipes are less wide.
(c) when water flows there is loss of pressure.
(d) None of these
Ans: C
28. Working of atomizer is based on
(a) Boyle’s law
(b) Bernoulli’s law
(c) Newton’s laws of motion
(d) Archimedes’ principle
Ans: B
29. Ideal liquid is that liquid
(a) whose density is zero
(b) whose viscosity is zero
(c) which is compressible
(d) None of these
Ans: B
30. Water is flowing through a horizontal pipe line having a restriction. Then
(a) pressure will be the same throughout the length of the pipe.
(b) pressure will be greater at the restriction.
(c) pressure will be greater in the wider portion.
(d) None of these
Ans: C
31 Paint-gun is based on
(a) Bernoulli’s theorem
(b) Archemedes’ principle
(c) Boyle’s law
(d) Newton’s laws of motion
Ans: A
32. A tank filled with water has a hole at a certain height from its bottom. The volume of water emerging out per second from the hole does not depend on
(a) the height of the level of liquid above the hole.
(b) the area of a hole.
(c) the density of a liquid.
(d) the acceleration due to gravity.
Ans: C
33. A boy carries a fish in one hand and a bucket of water in the other hand. If he places the fish in the bucket, the weight now carried by him.
(a) is less than before
(b) is more than before
(c) is the same as before
(d) depends upon his speed
Ans: C
34. A drop of oil is placed on the surface of water. Which of the following statements is correct?
(a) It will remain on it as a sphere
(b) It will spread as a thin layer
(c) It will partly be a spherical droplet and partly a thin film
(d) It will float as a distorted drop on the water surface
Ans: B
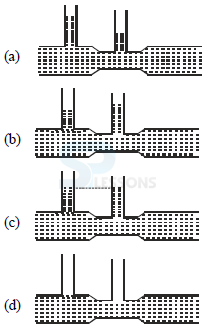
35. For a fluid which is flowing steadily, the level in the vertical
tubes is best represented by
Ans: A
36. Surface tension of a liquid is due to
(a) gravitational force between molecules
(b) electrical force between molecules
(c) adhesive force between molecules
(d) cohesive force between molecules
Ans: D
37. A liquid rises in a capillary tube higher than water does. The difference may be due to the fact that
(a) diameter of the capillary may be different in the two cases
(b) temperature of liquid is higher than that of water
(c) surface tension of water is less than that of the liquid
(d) both (a) and (c)
Ans: C
38. Construction of submarines is based on
(a) Archimede's principle
(b) Bernoulli's theorem
(c) Pascal's law
(d) Newton's laws
Ans: A
39. The action of a nib split at the top is explained by
(a) gravity flow
(b) diffusion of fluid
(c) capillary action
(d) osmosis of liquid
Ans: C
40. Why the dam of water reservoir is thick at the bottom?
(a) Quantity of water increases with depth
(b) Density of water increases with depth
(c) Pressure of water increases with depth
(d) Temperature of water increases with depth
Ans: C
41. Hydraulic lift is based on the principle of
(a) Pascal’s law
(b) Bernoulli’s theorem
(c) Toricelli’s theorem
(d) Stoke’s law
Ans: A
42. A and B are two wires. The radius of A is twice that of B. They are stretched by the same load. Then the stress on B is
(a) equal to that on A
(b) four times that on A
(c) two times that on A
(d) half that on A
Ans: B
1. Air is regarded as a mixture because
(a) its pressure may vary
(b) its temperature may change
(c) its volume changes under different conditions
(d) its composition may vary
Ans: D
2. Which of the following is a compound?
(a) Stainless steel
(b) Bronze
(c) Graphite
(d) Hydrogen sulphide
Ans: D
3. The process used to separate oil and water is
(a) distillation
(b) sublimation
(c) separating funnel
(d) chromatography
Ans: C
4. In which of the following the constituents are present in any ratio?
(a) Mixture
(b) Compound
(c) Solution
(d) Colloid
Ans: A
5. A mixture of common salt, sulphur, sand and iron filings is shaken with carbon disulphide and filtered through a filter paper. The filtrate is evaporated to dryness in a china dish. What will be left in the dish after evaporation?
(a) Sand
(b) Sulphur
(c) Iron filings
(d) Common salt
Ans: B
6. Two substances A and B when brought together form a substance C with the evolution of heat. The properties of C are entirely different from those of A and B. The substance C is
(a) a compound
(b) an element
(c) a mixture
(d) none of these.
Ans: A
7. Camphor can be purified by
(a) distillation
(b) filtration
(c) sedimentation
(d) sublimation
Ans: D
8. Which one of the following will result in the formation of a mixture?
(a) Crushing of a marble tile into small particles
(b) Breaking of ice cubes into small pieces
(c) Adding sodium metal to water
(d) Adding milk to water
Ans: D
9. Purity of a solid substance can be checked by its
(a) boiling point
(b) melting point
(c) solubility in water
(d) solubility in alcohol
Ans: B
10. A mixture of ethanol and water can be separated by
(a) filtration
(b) decantation
(c) fractional distillation
(d) sublimation
Ans: C
11. Salt can be obtained from sea water by
(a) filtration
(b) decantation
(c) evaporation
(d) sublimation
Ans: C
12. A sample contains two substances and has uniform properties. The sample is
(a) a compound
(b) a heterogeneous mixture
(c) an element
(d) a homogeneous mixture
Ans: D
13. Which of the following is considered to be a pure substance?
(a) Granite
(b) Sodium chloride
(c) Muddy water
(d) Milk of magnesia
Ans: B
14. Physical properties of a mixture
(a) vary with the amount of substance.
(b) depend on the volume of the substance
(c) depend on the organization of the substance
(d) vary depending upon its components
Ans: D
15. Compounds
(a) are the same as mixtures
(b) can be separated by their physical properties
(c) contain only one type of element
(d) are different kinds of atoms chemically combined with each other.
Ans: D
16. White gold is used in jewelry and contains two elements, gold and palladium. A jeweler has two different samples that are both identical in appearance and have a uniform composition throughout. What can be said about the samples?
(a) They are homogeneous mixtures and be classified as metallic alloys.
(b) The materials are heterogeneous mixtures and can be classified by their components
(c) The samples have variable compositions and are classified as metallic solutions.
(d) The samples are heterogeneous mixtures that can be separated using magnetic properties.
Ans: A
17. Which of the following is an example of a heterogeneous substance?
(a) Bottled water
(b) Table salt
(c) Pieces of copper
(d) Candle
Ans: D
18. Which of the following is an example of a homogeneous substance?
(a) Granite
(b) Copper sulphate
(c) Oil-water solution
(d) Muddy water
Ans: B
19. Filtration can be used to separate
(a) solids from solids
(b) liquids from solids
(c) liquids from liquids
(d) liquids from gases
Ans: D
20. Melting points can separate materials because
(a) substances melt at different temperatures
(b) molecules vibrate rapidly when heated
(c) heat causes molecules to disintegrate
(d) many substances fuse at the melting point
Ans: A
21. Distillation is a good separation technique for
(a) solids
(b) liquids
(c) solid alloys
(d) gases
Ans: B
22. Solubility is a good separation technique for
(a) pure metals
(b) noble gases
(c) different salts
(d) metallic alloys
Ans: C
23. Magnetism is most beneficial for separating
(a) gases and non-metallic liquids
(b) magnetic solids and solids such as sulfur
(c) non-metallic solids and solids such as sulfur
(d) non-magnetic solids from non-magnetic liquids
Ans: B
24. Select the one that is a chemical change.
(a) Melting of wax
(b) Freezing of water
(c) Cooking of food
(d) None of these
Ans: C
25. Select the one that is a physical change.
(a) Digestion of food
(b) Growth of plant
(c) Rusting of iron
(d) None of these
Ans: D
26. On passing through a colloidal solution, the beam of light gets ..
(a) reflected
(b) refracted
(c) scattered
(d) absorbed
Ans: C
27. The size of colloidal particles usually lies in the range
(a) [latex]10^{–5}[/latex] [latex]- 10^–7[/latex]cm
(b) [latex]10^–7[/latex] [latex]- 10^–9[/latex]cm
(c) [latex]10^–3[/latex] [latex]- 10^–5[/latex]cm
(d) [latex]10^–2[/latex] [latex]- 10^–6[/latex]cm
Ans: A
28. Brass is an example of
(a) compound
(b) element
(c) homogeneous mixture
(d) heterogeneous mixture
Ans: C
29. Select the one that is not a chemical change ?
(a) Dissolution of ammonia in water.
(b) Dissolution of carbon dioxide in water.
(c) Dissolution of oxygen in water.
(d) None of these is a chemical change.
Ans: C
30. A change is said to be a chemical change when
(a) it is accompanied by energy change
(b) it is accompanied by formation of new substances
(c) it is accompanied by change in physical properties
(d) All the above are correct
Ans: D
31. Solutions with low concentrations of solutes are
(a) concentrated
(b) dilute
(c) solvents
(d) None of these
Ans: B
32. Which of the following statements is true about a colloidal system?
(a) It carries a net electric charge
(b) It consists of one phase only
(c) It can be made out of two gases
(d) It is electrically neutral as a whole
Ans: D
33. Cloud or fog is an example of colloidal system of
(a) liquid dispersed in gas
(b) gas dispersed in gas
(c) solid dispersed in gas
(d) solid dispersed in liquid
Ans: A
34. Normal solution is :
(a) inert solution
(b) acidic solution
(c) one litre containing one equivalent
(d) basic solution
Ans: C
35. Which of the following is a colloid ?
(a) Sugar solution
(b) Urea solution
(c) Silicic acid
(d) NaCl solution
Ans: C
36. When dispersed phase is liquid and dispersion medium is gas then the colloidal system is called
(a) smoke
(b) clouds
(c) jellies
(d) emulsions
Ans: B