Introduction
Introduction
Quadratic Equation is one of important topic in Quantitative Aptitude Section. In Quadratic Equation – Quiz 2 article candidates can find a question with an answer. By solving this question candidates can improve and maintain, speed, and accuracy in the exams. Quadratic Equation – Quiz 2 questions are very useful for different exams such as IBPS PO, Clerk, SSC CGL, SBI PO, NIACL Assistant, NICL AO, IBPS SO, RRB, Railways, Civil Services etc.
 Q1
Q1
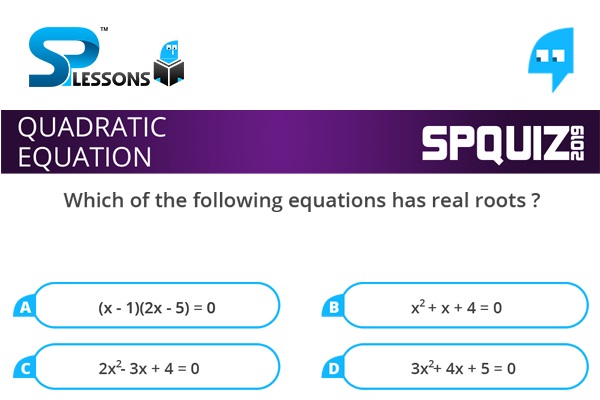
1. Which of the following equations has real roots ?
- A. (x - 1)(2x - 5) = 0
B. [latex]{x}^{2} [/latex] + x + 4 = 0
C. 2[latex]{x}^{2} [/latex] - 3x + 4 = 0
D. 3[latex]{x}^{2} [/latex] + 4x + 5 = 0
Given equation (x - 1)(2x - 5) = 0
[latex]\Rightarrow 2{x}^{2} - 7x + 5 = 0[/latex]
i.e, D = [latex]{(-7)}^{2} - 4 \times 2 \times 5 [/latex] = (49 - 40) = 9 > 0
i.e, Given equation has real roots.
 Q2
Q2
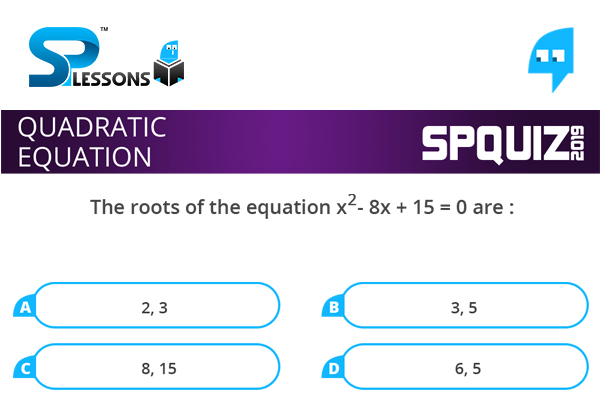
The roots of the equation [latex]{x}^{2} [/latex] - 8x + 15 = 0 are :
- A. 2, 3
B. 3, 5
C. 8, 15
D. 6, 5
[latex]{x}^{2} [/latex] - 8x + 15 = 0 [latex]\Rightarrow {x}^{2} - 5x - 3x + 15 = 0[/latex]
[latex]\Rightarrow [/latex] x (x - 5) -3 (x - 5) = 0
[latex]\Rightarrow [/latex] (x - 5) (x - 3) [latex]\Rightarrow [/latex] x = 5 or x = 3
 Q3
Q3
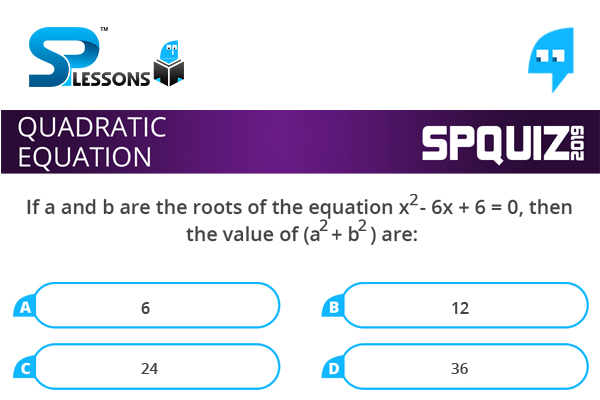
If a and b are the roots of the equation [latex]{x}^{2} [/latex] - 6x + 6 = 0, then the value of ([latex]{a}^{2} [/latex] + [latex]{b}^{2} [/latex] ) are :
- A. 6
B. 12
C. 24
D. 36
(a + b) = 6 and ab = 6
i.e, ([latex]{a}^{2} [/latex] + [latex]{b}^{2} [/latex] ) = [latex]{(a + b)}^{2} [/latex] - 2ab = [latex]{6}^{2} - 2 \times 6[/latex] = (36 - 12 ) = 24
 Q4
Q4
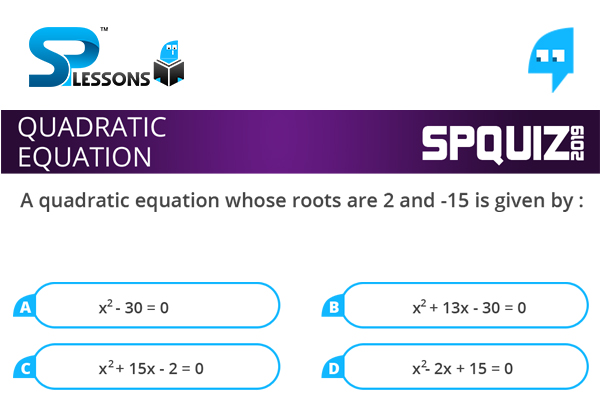
A quadratic equation whose roots are 2 and -15 is given by :
- A. [latex]{x}^{2} [/latex] - 30 = 0
B. [latex]{x}^{2} [/latex] + 13x - 30 = 0
C. [latex]{x}^{2} [/latex] + 15x - 2 = 0
D. [latex]{x}^{2} [/latex] - 2x + 15 = 0
[latex]\alpha + \beta [/latex] = 2 + (-15) = 13, [latex]\alpha \beta [/latex] = 2 [latex]\times [/latex] (-15) = -30
Required equation is [latex]{x}^{2} [/latex] + [latex](\alpha + \beta) [/latex]x - [latex]\alpha \beta [/latex] = 0
[latex]{x}^{2} [/latex] + 13x - 30 = 0
 Q5
Q5
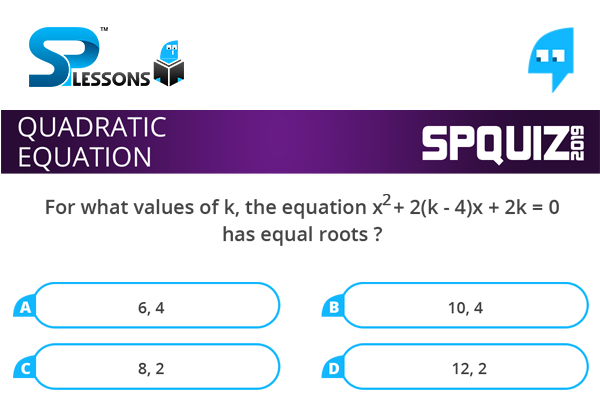
For what values of k, the equation [latex]{x}^{2} [/latex] + 2(k - 4)x + 2k = 0 has equal roots ?
- A. 6, 4
B. 10, 4
C. 8, 2
D. 12, 2
Since the roots are equal, we have D = 0
i.e, 4[latex]({k - 4})^{2} [/latex] - 8k = 0 [latex]\Rightarrow [/latex] [latex]({k - 4})^{2} [/latex] - 2k = 0
[latex]{k}^{2} [/latex] + 16 - 10k = 0 [latex]{k}^{2} [/latex] - 10k + 16 = 0
[latex]\Rightarrow [/latex] (k - 8) (k - 2) = 0 [latex]\Rightarrow [/latex] k = 8 or k =2