Description
Description
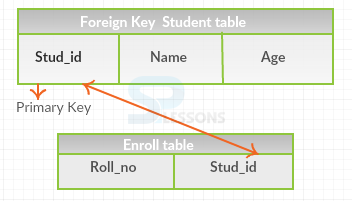
When a column is defined with SQL Foreign Key constraint then that foreign key constraint column will accept only the values of given Primary Key Constraint column.
- A table can have stand out primary key constraint column.
- A table can have any number of SQL Foreign Key constraints columns.
- A table in which primary key constraint is defined is called parent key.
- A table in which foreign key constraint column is defined is called child table.
- A parent table can have any number of child tables, but a child table can have only one parent table.
- Without inserting parent record in parent table child record cannot be inserted into child table.
- Without deleting child record from child table, parent record cannot be deleted from parent table.
 Syntax
Syntax
Create table <table_name1>(<column_name1> datatype(size), <column_name2>datatype(size), primary key constraint(column_name1));
create table <table_name2>(<column_name1( datatype(size), <column_name2>datatype(size), datatype(size), FOREIGN KEY constraint(column_name1) REFERENCES(column_name1); );
Table_name => Any accurate table.
Column_name =>The operation that can be perform on a column in the table.
constraint_type =>constraint type will specify the type of constraint, that going to be executed in the database.
 Examples
Examples
By viewing the below example, the concept of SQL Foreign Key constraint can be easily understood.
[c]sql> CREATE TABLE Student(stud_id int AUTO_INCREMENT,name varchar(30)NOT NULL,age int NOT NULL,PRIMARY KEY(stud_id));
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.37 sec)
sql> insert into Student (name,age) values ('mike',25);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.11 sec)
sql> insert into Student (name,age) values ('kate',35);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.05 sec)
sql> select * from Student;
+---------+------+-----+
| stud_id | name | age |
+---------+------+-----+
| 1 | mike | 25 |
| 2 | kate | 35 |
+---------+------+-----+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
sql> CREATE TABLE enroll(rol_no int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,stud_id int NOT N
ULL,PRIMARY KEY(rol_no),FOREIGN KEY(stud_id)REFERENCES Student(stud_id));
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.34 sec)
sql> INSERT INTO enroll (stud_id) values (1);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.38 sec)
sql> INSERT INTO enroll (stud_id) values (2);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.18 sec)
sql> INSERT INTO enroll (stud_id) values (3);
ERROR 1452 (23000): Cannot add or update a child row: a foreign key constraint f
ails (`employee`.`enroll`, CONSTRAINT `enroll_ibfk_1` FOREIGN KEY (`stud_id`)
REFERENCES `student` (`stud_id`))
sql> select * from enroll;
+--------+---------+
| rol_no | stud_id |
+--------+---------+
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 |
+--------+---------+
2 rows in set (0.06 sec)
[/c]
In the above example, 2 tables have been has created i.e, student and enroll. In student table primary key constraint is assigned to column stud_id, so no need to assign stud_id values just write name and age values, stud_id values will be taken automatically. In the table enroll foreign key is assigned to stud_id with reference to primary key. In such case in enroll table assigning stud_id values has to satisfy the stud_id of student values, if not, it will terminate the values.
 Key Points
Key Points
- SQL Foreign Key Constraint - Foreign key values will accept only the primary key values.