Introduction
Introduction
What is Liberalized Remittance Scheme?
- The Liberalised Remittance Scheme by the Reserve Bank of India allows resident Indians to send up to $250,000 USD out of India.
- It can only be done through Authorised Dealers, which are mostly banks. The remittance covers every fiscal year, i.e April – March.
- It is a measure by the R.B.I for capital control In relation to upwardly mobile Indian residents. In easier terms, the scheme helps the R.B.I keep track of Indian currency moving out of India.
- It was introduced In 2004, to help Indians resident and non-resident Indians better move their money in the sphere of work/studies/travel, etc.
 LRS
LRS
- One is allowed to remit a maximum of $250,000. Hitting this mark would mean that one could no longer remit any further amount for the remaining year.
- The limit of allowance stands true even in the scenario of having brought investments/proceeds back into the country vis-à-vis the money that one had remitted.
- The dollar designation of the remittable limits is not a reflection of the currencies the remittance amount can be made in.
- ANY FREELY CONVERTIBLE foreign currency, that is offered through one’s authorized dealer is allowed. Only the converted amount can never exceed $250,000 USD.
Primary Uses:
Exclusions:
| Primary Reasons ALLOWED use the Liberalized Remittance Scheme as listed by the R.B.I |
|---|
| 1. Private visits to any country (except Nepal and Bhutan) |
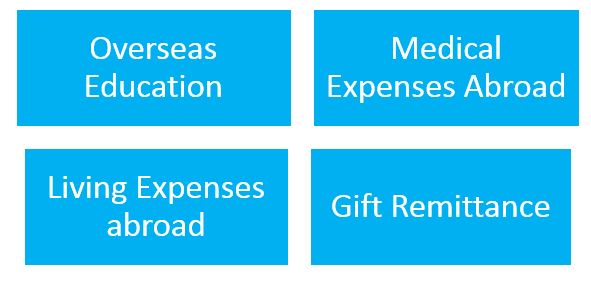
| 2. Gift or donation |
| 3. Going abroad for employment |
| 4. Emigration |
| 5. Maintenance of close relatives abroad |
| 6. Travel for business, or attending a conference or specialized training or for meeting expenses for meeting medical expenses, or check-up abroad, or for accompanying as attendant to a patient going abroad for medical treatment/ check-up |
| 7. Expenses in connection with medical treatment abroad |
| 8. Studies abroad |
| 9. Any other current account transaction which is not covered under the definition of the current account in FEMA 1999 |
| Prohibited Items under the Scheme |
|---|
| 1. 1. Remittance for items prohibited under Schedule-I : purchase of lottery tickets/sweep stakes, proscribed magazines etc. |
| 2. Remittance for purchase of FCCBs in the overseas market. (FCCB – Foreign Currency Convertible Bond) |
| 3. Remittance for trading in foreign exchange. |
| 4. Remittance for any capital account remittance to countries identified as “non-cooperative countries and territories” by the Financial Action Task Force, at that time |
| 5. Direct/indirect remittances to individuals/entities who pose significant risks of committing terrorist acts. This is under separate advise by the RBI to the authorized banks. |
Eligibility: The Liberalised Remittance Scheme is available to any Indian Resident with a PAN Card. It is also available to minors who hold proper documentation.
 Indian Students
Indian Students
Foreign Study amongst upscale Indians is on the rise and in 2019 , outlays on overseas travel under LRS surged 56% to $568million In May. Plus education expense and maintenance of close relatives grew 88% to $334 million and 21% to $300 million respectively.
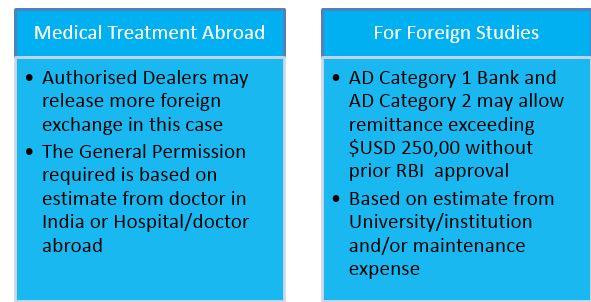
- The maximum Remittance Limit for students (including minor students) is $USD 250,000 per financial year.
- The limit can be used in either a single or multiple Forex transactions.
- Minor Students require their natural parents to sign the LRS declaration.
- The prohibited activities for LRS hold true for students too. Also included is remittance through racing/riding etc.
- The exception to the limit: Under Special Circumstances, one is allowed to draw more foreign exchange than the $USD 250,000., of which students too can make avail. These are:
How to send money abroad from India under LRS?
1. One must select an RBI authorized Bank or money changer. The one with the best exchange rate should be opted for.
2. The account needs to have been maintained for a year prior to remittance. Else, bank statements for the previous year or copies of the latest income tax assessment order or tax returns filed are to be submitted.
3. The A2 form with the reason for remittance is to be submitted.
4. KYC documents are to be submitted –
-
Passport Copy of Sender
PAN Card Copy
Beneficiary Passport Copy (if required)
Relationship Proof (if required)